Claudin 1 Antibody - #AF0127
| 产品: | Claudin 1 抗体 |
| 货号: | AF0127 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Claudin 1 |
| 应用: | WB IHC |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 预测: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Chicken |
| 分子量: | 22kDa; 23kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | O95832 |
| RRID: | AB_2833311 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0127, RRID:AB_2833311.
展开/折叠
Claudin-1; Claudin1; CLD 1; CLD1; CLD1_HUMAN; CLDN 1; Cldn1; ILVASC; SEMP 1; SEMP1; Senescence associated epithelial membrane protein 1; Senescence associated epithelial membrane protein; Senescence-associated epithelial membrane protein;
抗原和靶标
Strongly expressed in liver and kidney. Expressed in heart, brain, spleen, lung and testis.
- O95832 CLD1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MANAGLQLLGFILAFLGWIGAIVSTALPQWRIYSYAGDNIVTAQAMYEGLWMSCVSQSTGQIQCKVFDSLLNLSSTLQATRALMVVGILLGVIAIFVATVGMKCMKCLEDDEVQKMRMAVIGGAIFLLAGLAILVATAWYGNRIVQEFYDPMTPVNARYEFGQALFTGWAAASLCLLGGALLCCSCPRKTTSYPTPRPYPKPAPSSGKDYV
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
翻译修饰 - O95832 作为底物
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| K115 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T153 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K189 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T191 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| T191 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S192 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| S192 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T195 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K201 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S205 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| S205 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S206 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| S206 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K208 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y210 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot |
研究背景
Claudins function as major constituents of the tight junction complexes that regulate the permeability of epithelia. While some claudin family members play essential roles in the formation of impermeable barriers, others mediate the permeability to ions and small molecules. Often, several claudin family members are coexpressed and interact with each other, and this determines the overall permeability. CLDN1 is required to prevent the paracellular diffusion of small molecules through tight junctions in the epidermis and is required for the normal barrier function of the skin. Required for normal water homeostasis and to prevent excessive water loss through the skin, probably via an indirect effect on the expression levels of other proteins, since CLDN1 itself seems to be dispensable for water barrier formation in keratinocyte tight junctions.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in hepatocytes. Associates with CD81 and the CLDN1-CD81 receptor complex is essential for HCV entry into host cell. Acts as a receptor for dengue virus.
Cell junction>Tight junction. Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Basolateral cell membrane.
Note: Associates with CD81 and the CLDN1-CD81 complex localizes to the basolateral cell membrane.
Strongly expressed in liver and kidney. Expressed in heart, brain, spleen, lung and testis.
Homopolymers interact with CLDN3, but not CLDN2, homopolymers. Can form homo- and heteropolymers with other claudin family members. Directly interacts with TJP1/ZO-1, TJP2/ZO-2 and TJP3/ZO-3. Interacts with MPDZ and PATJ (By similarity). Interacts with OCLN, CLDN4, CLDN6 and CLDN9. Interacts with CD81.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with hepatitis c virus E1 and E2 proteins.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with dengue virus small envelope protein M.
Belongs to the claudin family.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Leukocyte transendothelial migration. (View pathway)
文献引用
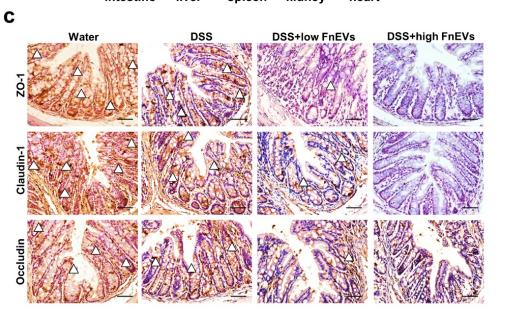
Application: IHC Species: mouse Sample: colon
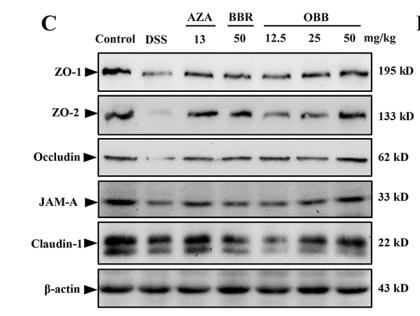
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: colonic tissues
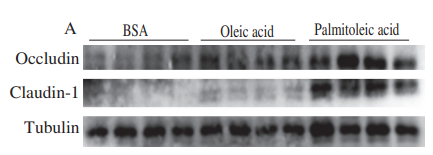
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: lung
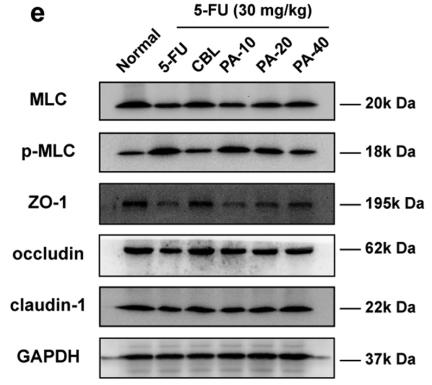
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: Intestinal
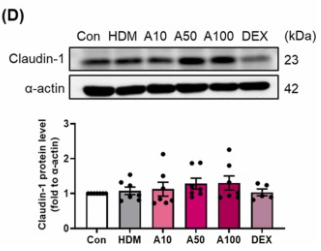
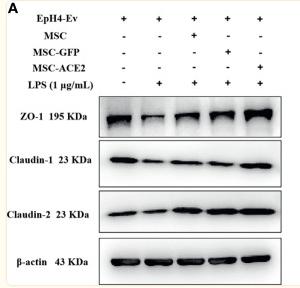
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: EpH4-Ev cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
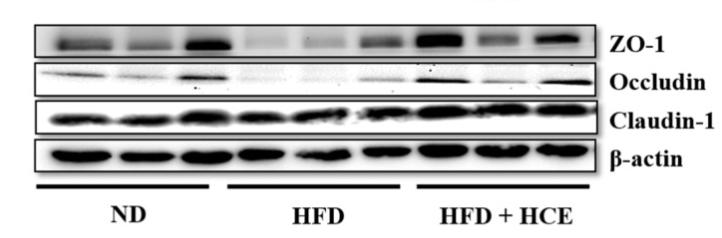
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: epididymal white adipose tissue
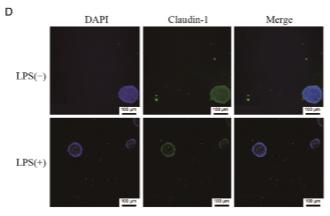
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.