| 产品: | CEP55 抗体 |
| 货号: | DF3918 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CEP55 |
| 应用: | WB IHC |
| 反应: | Human |
| 分子量: | 54 KD; 54kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | Q53EZ4 |
| RRID: | AB_2836271 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF3918, RRID:AB_2836271.
展开/折叠
C10orf3; cancer/testis antigen 111; Centrosomal protein 55kDa; Centrosomal protein of 55 kDa; CEP 55; Cep55; CEP55_HUMAN; CT111; FLJ10540; Up regulated in colon cancer 6; Up-regulated in colon cancer 6; URCC 6; URCC6;
抗原和靶标
Expressed in embryonic brain (PubMed:28264986). Expressed in fetal brain ganglionic eminence, kidney tubules and multinucleate neurons in the temporal cortex (PubMed:28264986). Expressed in adult brain, cerebellum, kidney tubules, intestine and muscles (at protein level) (PubMed:28295209, PubMed:28264986). Widely expressed, mostly in proliferative tissues. Highly expressed in testis. Intermediate levels in adult and fetal thymus, as well as in various cancer cell lines. Low levels in different parts of the digestive tract, bone marrow, lymph nodes, placenta, fetal heart and fetal spleen. Hardly detected in brain.
- Q53EZ4 CEP55_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSSRSTKDLIKSKWGSKPSNSKSETTLEKLKGEIAHLKTSVDEITSGKGKLTDKERHRLLEKIRVLEAEKEKNAYQLTEKDKEIQRLRDQLKARYSTTTLLEQLEETTREGERREQVLKALSEEKDVLKQQLSAATSRIAELESKTNTLRLSQTVAPNCFNSSINNIHEMEIQLKDALEKNQQWLVYDQQREVYVKGLLAKIFELEKKTETAAHSLPQQTKKPESEGYLQEEKQKCYNDLLASAKKDLEVERQTITQLSFELSEFRRKYEETQKEVHNLNQLLYSQRRADVQHLEDDRHKTEKIQKLREENDIARGKLEEEKKRSEELLSQVQFLYTSLLKQQEEQTRVALLEQQMQACTLDFENEKLDRQHVQHQLHVILKELRKARNQITQLESLKQLHEFAITEPLVTFQGETENREKVAASPKSPTAALNESLVECPKCNIQYPATEHRDLLVHVEYCSK
翻译修饰 - Q53EZ4 作为底物
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| S5 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K13 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K17 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S21 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K22 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S23 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K29 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K31 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K38 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S40 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K48 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T52 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K92 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K119 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K125 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K129 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S144 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K145 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T146 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T148 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S152 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T154 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K180 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K196 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K201 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K207 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K208 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S215 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K222 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y228 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K233 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K235 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K245 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K246 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K268 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K274 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y284 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S285 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K300 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K306 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K317 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y336 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T337 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K341 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T360 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K367 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S396 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K398 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S425 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) , P06493 (CDK1) | Uniprot |
| K427 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S428 | Phosphorylation | P06493 (CDK1) , P28482 (MAPK1) | Uniprot |
| T430 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S436 | Phosphorylation | P53350 (PLK1) | Uniprot |
| K442 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y461 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S463 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot |
研究背景
Plays a role in mitotic exit and cytokinesis. Recruits PDCD6IP and TSG101 to midbody during cytokinesis. Required for successful completion of cytokinesis. Not required for microtubule nucleation. Plays a role in the development of the brain and kidney.
There is a hierachy of phosphorylation, where both Ser-425 and Ser-428 are phosphorylated at the onset of mitosis, prior to Ser-436. Phosphorylation at Ser-425 and Ser-428 is required for dissociation from the centrosome at the G2/M boundary. Phosphorylation at the 3 sites, Ser-425, Ser-428 and Ser-436, is required for protein function at the final stages of cell division to complete cytokinesis successfully.
Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome>Centriole. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Cleavage furrow. Midbody>Midbody ring.
Note: Present at the centrosomes at interphase. A small portion is associated preferentially with the mother centriole, whereas the majority localizes to the pericentriolar material. During mitosis, loses affinity for the centrosome at the onset of prophase and diffuses throughout the cell. This dissociation from the centrosome is phosphorylation-dependent. May remain localized at the centrosome during mitosis in certain cell types. Appears at the cleavage furrow in late anaphase and in the midbody in cytokinesis.
Expressed in embryonic brain. Expressed in fetal brain ganglionic eminence, kidney tubules and multinucleate neurons in the temporal cortex. Expressed in adult brain, cerebellum, kidney tubules, intestine and muscles (at protein level). Widely expressed, mostly in proliferative tissues. Highly expressed in testis. Intermediate levels in adult and fetal thymus, as well as in various cancer cell lines. Low levels in different parts of the digestive tract, bone marrow, lymph nodes, placenta, fetal heart and fetal spleen. Hardly detected in brain.
Homodimer. Interacts (phosphorylated on Ser-425 and Ser-428) with PLK1. Interacts with AKAP9/CG-NAP; the interaction occurs in interphase and is lost upon mitotic entry. Interacts with PCNT/Kendrin; the interaction occurs in interphase and is lost upon mitotic entry. Directly interacts with PDCD6IP; this interaction is required for PDCD6IP targeting to the midbody; CEP55 binds PDCD6IP in a 2:1 stoichiometry; PDCD6IP competes with TSG101 for the same binding site. Interacts with TSG101; TSG101 competes with PDCD6IP for the same binding site; interaction is required for cytokinesis but not for viral budding. Interacts with MVB12A, VPS37B, VPS37C and VPS28.
文献引用
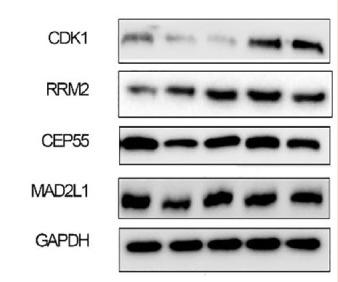
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: breast cancer tissue
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.