产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5195, RRID:AB_2837681.
展开/折叠
Mutant myeloid differentiation primary response 88; MYD 88; Myd88; MYD88_HUMAN; MYD88D; Myeloid differentiation marker 88; Myeloid differentiation primary response 88; Myeloid differentiation primary response gene (88); Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; Myeloid differentiation primary response gene; Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88; OTTHUMP00000161718; OTTHUMP00000208595; OTTHUMP00000209058; OTTHUMP00000209059; OTTHUMP00000209060;
抗原和靶标
- Q99836 MYD88_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAAGGPGAGSAAPVSSTSSLPLAALNMRVRRRLSLFLNVRTQVAADWTALAEEMDFEYLEIRQLETQADPTGRLLDAWQGRPGASVGRLLELLTKLGRDDVLLELGPSIEEDCQKYILKQQQEEAEKPLQVAAVDSSVPRTAELAGITTLDDPLGHMPERFDAFICYCPSDIQFVQEMIRQLEQTNYRLKLCVSDRDVLPGTCVWSIASELIEKRCRRMVVVVSDDYLQSKECDFQTKFALSLSPGAHQKRLIPIKYKAMKKEFPSILRFITVCDYTNPCTKSWFWTRLAKALSLP
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
翻译修饰 - Q99836 作为底物
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| K95 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| C113 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K115 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K119 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K127 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K190 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K214 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| C216 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K231 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K238 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S244 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K250 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K256 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y257 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K262 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y276 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K282 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K291 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
研究背景
Adapter protein involved in the Toll-like receptor and IL-1 receptor signaling pathway in the innate immune response. Acts via IRAK1, IRAK2, IRF7 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Increases IL-8 transcription. Involved in IL-18-mediated signaling pathway. Activates IRF1 resulting in its rapid migration into the nucleus to mediate an efficient induction of IFN-beta, NOS2/INOS, and IL12A genes. MyD88-mediated signaling in intestinal epithelial cells is crucial for maintenance of gut homeostasis and controls the expression of the antimicrobial lectin REG3G in the small intestine (By similarity).
Ubiquitinated; undergoes 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination. OTUD4 specifically hydrolyzes 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitinated MYD88.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Ubiquitous.
Homodimer. Also forms heterodimers with TIRAP. Binds to TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, IRAK1, IRAK2 and IRAK4 via their respective TIR domains. Interacts with IL18R1. Interacts with BMX, IL1RL1, IKBKE and IRF7. Interacts with LRRFIP1 and LRRFIP2; this interaction positively regulates Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in response to agonist. Interacts with FLII. LRRFIP1 and LRRFIP2 compete with FLII for MYD88-binding. Interacts with IRF1. Upon IL1B treatment, forms a complex with PELI1, IRAK1, IRAK4 and TRAF6; this complex recruits MAP3K7/TAK1, TAB1 and TAB2 to mediate NF-kappa-B activation. Direct binding of SMAD6 to PELI1 prevents the complex formation and hence negatively regulates IL1R-TLR signaling and eventually NF-kappa-B-mediated gene expression. May interact with PIK3AP1. Interacts (via TIR domain) with DHX9 (via H2A and OB-fold regions); this interaction is direct. Interacts with OTUD4 deubiquitinase; the interaction is direct.
(Microbial infection) In case of infection, interacts with uropathogenic E.coli protein TcpC; suppressing Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated cytokine production.
(Microbial infection) In case of infection, interacts with uropathogenic E.faecalis protein TcpF; suppressing Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated cytokine production.
The intermediate domain (ID) is required for the phosphorylation and activation of IRAK.
研究领域
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > African trypanosomiasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Malaria.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
文献引用
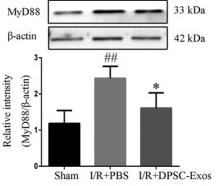
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: colonic tissues
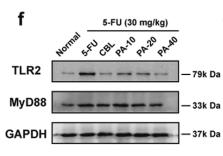
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample:
Application: WB Species: rat Sample:
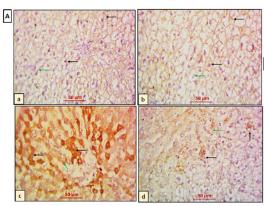
Application: IHC Species: Rat Sample: hepatic tissues
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.