| 产品: | NF-kB p65 小鼠 单克隆 抗体 |
| 货号: | BF8005 |
| 描述: | Mouse monoclonal antibody to NF-kB p65 |
| 应用: | WB |
| 文献验证: | WB |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Monkey |
| 分子量: | 65 kDa; 60kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | Q04206 |
| RRID: | AB_2846809 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF8005, RRID:AB_2846809.
展开/折叠
Avian reticuloendotheliosis viral (v rel) oncogene homolog A; MGC131774; NF kappa B p65delta3; NFKB3; Nuclear Factor NF Kappa B p65 Subunit; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells 3; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3; OTTHUMP00000233473; OTTHUMP00000233474; OTTHUMP00000233475; OTTHUMP00000233476; OTTHUMP00000233900; p65; p65 NF kappaB; p65 NFkB; relA; TF65_HUMAN; Transcription factor p65; v rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells 3 (p65)); V rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A; v rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian); V rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells 3, p65;
研究背景
NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. The NF-kappa-B heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 and RELA-REL complexes, for instance, function as transcriptional activators. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B on NF-kappa-B through retention in the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with RELA. RELA shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex. Beside its activity as a direct transcriptional activator, it is also able to modulate promoters accessibility to transcription factors and thereby indirectly regulate gene expression. Associates with chromatin at the NF-kappa-B promoter region via association with DDX1. Essential for cytokine gene expression in T-cells. The NF-kappa-B homodimeric RELA-RELA complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression.
Ubiquitinated by RNF182, leading to its proteasomal degradation. Degradation is required for termination of NF-kappa-B response.
Monomethylated at Lys-310 by SETD6. Monomethylation at Lys-310 is recognized by the ANK repeats of EHMT1 and promotes the formation of repressed chromatin at target genes, leading to down-regulation of NF-kappa-B transcription factor activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-311 disrupts the interaction with EHMT1 without preventing monomethylation at Lys-310 and relieves the repression of target genes (By similarity).
Phosphorylation at Ser-311 disrupts the interaction with EHMT1 and promotes transcription factor activity (By similarity). Phosphorylation on Ser-536 stimulates acetylation on Lys-310 and interaction with CBP; the phosphorylated and acetylated forms show enhanced transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-276 by RPS6KA4 and RPS6KA5 promotes its transactivation and transcriptional activities.
Reversibly acetylated; the acetylation seems to be mediated by CBP, the deacetylation by HDAC3 and SIRT2. Acetylation at Lys-122 enhances DNA binding and impairs association with NFKBIA. Acetylation at Lys-310 is required for full transcriptional activity in the absence of effects on DNA binding and NFKBIA association. Acetylation at Lys-310 promotes interaction with BRD4. Acetylation can also lower DNA-binding and results in nuclear export. Interaction with BRMS1 promotes deacetylation of Lys-310. Lys-310 is deacetylated by SIRT2.
S-nitrosylation of Cys-38 inactivates the enzyme activity.
Sulfhydration at Cys-38 mediates the anti-apoptotic activity by promoting the interaction with RPS3 and activating the transcription factor activity.
Sumoylation by PIAS3 negatively regulates DNA-bound activated NF-kappa-B.
Proteolytically cleaved within a conserved N-terminus region required for base-specific contact with DNA in a CPEN1-mediated manner, and hence inhibits NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Note: Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor (I-kappa-B) (PubMed:1493333). Colocalized with DDX1 in the nucleus upon TNF-alpha induction (PubMed:19058135). Colocalizes with GFI1 in the nucleus after LPS stimulation (PubMed:20547752). Translocation to the nucleus is impaired in L.monocytogenes infection (PubMed:20855622).
The transcriptional activation domain 3/TA3 does not participate to the direct transcriptional activity of RELA but is involved in the control by RELA of the accessibility of target gene promoters. Mediates interaction with ZBTB7A.
The transcriptional activation domain 1/TA1 and the transcriptional activation domain 2/TA2 have direct transcriptional activation properties (By similarity). The 9aaTAD motif found within the transcriptional activation domain 2 is a conserved motif present in a large number of transcription factors that is required for their transcriptional transactivation activity (PubMed:17467953).
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Sphingolipid signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Antifolate resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Cocaine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Shigellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Amoebiasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Prolactin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
文献引用
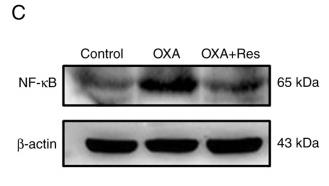
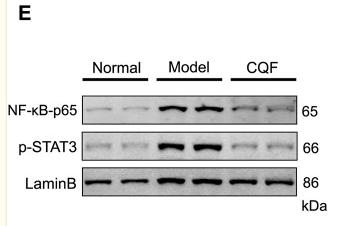
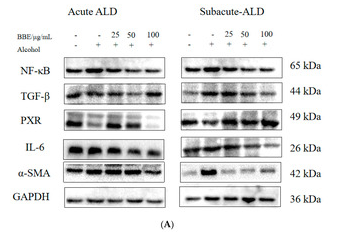
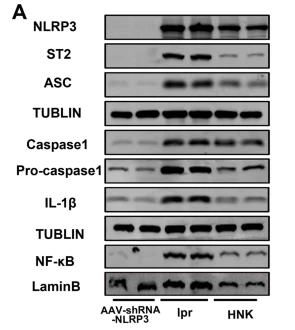
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: VSMCs
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.