| 产品: | 磷酸化 CFTR (Ser737) 抗体 |
| 货号: | AF8042 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-CFTR (Ser737) |
| 应用: | WB IHC |
| 文献验证: | WB |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 预测: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| 分子量: | 168kDa; 168kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | P13569 |
| RRID: | AB_2840105 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8042, RRID:AB_2840105.
展开/折叠
ABC 35; ABC35; ABCC 7; ABCC7; ATP binding cassette sub family C member 7; ATP Binding Cassette Superfamily C Member 7; ATP binding cassette transporter sub family C member 7; ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 7; cAMP dependent chloride channel; cAMP-dependent chloride channel; CF; CFTR; CFTR/MRP; CFTR_HUMAN; Channel conductance controlling ATPase; Channel conductance-controlling ATPase; Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (ATP-binding cassette sub family C, member 7); Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator ATP binding cassette sub family C member 7; Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator; dJ760C5.1; MRP 7; MRP7; TNR CFTR;
抗原和靶标
A synthesized peptide derived from human CFTR around the phosphorylation site of Ser737.
Expressed in the respiratory airway, including bronchial epithelium, and in the female reproductive tract, including oviduct (at protein level) (PubMed:22207244, PubMed:15716351). Detected in pancreatic intercalated ducts in the exocrine tissue, on epithelial cells in intralobular striated ducts in sublingual salivary glands, on apical membranes of crypt cells throughout the small and large intestine, and on the reabsorptive duct in eccrine sweat glands (PubMed:1284548, PubMed:28130590). Detected on the equatorial segment of the sperm head (at protein level) (PubMed:19923167). Detected in nasal and bronchial superficial epithelium (PubMed:15716351). Expressed by the central cells on the sebaceous glands, dermal adipocytes and, at lower levels, by epithelial cells (PubMed:28130590).
- P13569 CFTR_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MQRSPLEKASVVSKLFFSWTRPILRKGYRQRLELSDIYQIPSVDSADNLSEKLEREWDRELASKKNPKLINALRRCFFWRFMFYGIFLYLGEVTKAVQPLLLGRIIASYDPDNKEERSIAIYLGIGLCLLFIVRTLLLHPAIFGLHHIGMQMRIAMFSLIYKKTLKLSSRVLDKISIGQLVSLLSNNLNKFDEGLALAHFVWIAPLQVALLMGLIWELLQASAFCGLGFLIVLALFQAGLGRMMMKYRDQRAGKISERLVITSEMIENIQSVKAYCWEEAMEKMIENLRQTELKLTRKAAYVRYFNSSAFFFSGFFVVFLSVLPYALIKGIILRKIFTTISFCIVLRMAVTRQFPWAVQTWYDSLGAINKIQDFLQKQEYKTLEYNLTTTEVVMENVTAFWEEGFGELFEKAKQNNNNRKTSNGDDSLFFSNFSLLGTPVLKDINFKIERGQLLAVAGSTGAGKTSLLMVIMGELEPSEGKIKHSGRISFCSQFSWIMPGTIKENIIFGVSYDEYRYRSVIKACQLEEDISKFAEKDNIVLGEGGITLSGGQRARISLARAVYKDADLYLLDSPFGYLDVLTEKEIFESCVCKLMANKTRILVTSKMEHLKKADKILILHEGSSYFYGTFSELQNLQPDFSSKLMGCDSFDQFSAERRNSILTETLHRFSLEGDAPVSWTETKKQSFKQTGEFGEKRKNSILNPINSIRKFSIVQKTPLQMNGIEEDSDEPLERRLSLVPDSEQGEAILPRISVISTGPTLQARRRQSVLNLMTHSVNQGQNIHRKTTASTRKVSLAPQANLTELDIYSRRLSQETGLEISEEINEEDLKECFFDDMESIPAVTTWNTYLRYITVHKSLIFVLIWCLVIFLAEVAASLVVLWLLGNTPLQDKGNSTHSRNNSYAVIITSTSSYYVFYIYVGVADTLLAMGFFRGLPLVHTLITVSKILHHKMLHSVLQAPMSTLNTLKAGGILNRFSKDIAILDDLLPLTIFDFIQLLLIVIGAIAVVAVLQPYIFVATVPVIVAFIMLRAYFLQTSQQLKQLESEGRSPIFTHLVTSLKGLWTLRAFGRQPYFETLFHKALNLHTANWFLYLSTLRWFQMRIEMIFVIFFIAVTFISILTTGEGEGRVGIILTLAMNIMSTLQWAVNSSIDVDSLMRSVSRVFKFIDMPTEGKPTKSTKPYKNGQLSKVMIIENSHVKKDDIWPSGGQMTVKDLTAKYTEGGNAILENISFSISPGQRVGLLGRTGSGKSTLLSAFLRLLNTEGEIQIDGVSWDSITLQQWRKAFGVIPQKVFIFSGTFRKNLDPYEQWSDQEIWKVADEVGLRSVIEQFPGKLDFVLVDGGCVLSHGHKQLMCLARSVLSKAKILLLDEPSAHLDPVTYQIIRRTLKQAFADCTVILCEHRIEAMLECQQFLVIEENKVRQYDSIQKLLNERSLFRQAISPSDRVKLFPHRNSSKCKSKPQIAALKEETEEEVQDTRL
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Epithelial ion channel that plays an important role in the regulation of epithelial ion and water transport and fluid homeostasis. Mediates the transport of chloride ions across the cell membrane. Channel activity is coupled to ATP hydrolysis. The ion channel is also permeable to HCO(3-); selectivity depends on the extracellular chloride concentration. Exerts its function also by modulating the activity of other ion channels and transporters. Plays an important role in airway fluid homeostasis. Contributes to the regulation of the pH and the ion content of the airway surface fluid layer and thereby plays an important role in defense against pathogens. Modulates the activity of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) complex, in part by regulating the cell surface expression of the ENaC complex. Inhibits the activity of the ENaC channel containing subunits SCNN1A, SCNN1B and SCNN1G. Inhibits the activity of the ENaC channel containing subunits SCNN1D, SCNN1B and SCNN1G, but not of the ENaC channel containing subunits SCNN1A, SCNN1B and SCNN1G. May regulate bicarbonate secretion and salvage in epithelial cells by regulating the transporter SLC4A7. Can inhibit the chloride channel activity of ANO1. Plays a role in the chloride and bicarbonate homeostasis during sperm epididymal maturation and capacitation.
N-glycosylated.
Phosphorylated; cAMP treatment promotes phosphorylation and activates the channel. Dephosphorylation decreases the ATPase activity (in vitro). Phosphorylation at PKA sites activates the channel. Phosphorylation at PKC sites enhances the response to phosphorylation by PKA. Phosphorylated by AMPK; this inhibits channel activity.
Ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation in the lysosome. Deubiquitination by USP10 in early endosomes enhances its endocytic recycling to the cell membrane. Ubiquitinated by RNF185 during ER stress.
Apical cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Early endosome membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Recycling endosome membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Nucleus.
Note: The channel is internalized from the cell surface into an endosomal recycling compartment, from where it is recycled to the cell membrane (PubMed:17462998, PubMed:19398555, PubMed:20008117). In the oviduct and bronchus, detected on the apical side of epithelial cells, but not associated with cilia (PubMed:22207244). In Sertoli cells, a processed product is detected in the nucleus (By similarity). ER stress induces GORASP2-mediated unconventional (ER/Golgi-independent) trafficking of core-glycosylated CFTR to cell membrane (PubMed:21884936).
Expressed in the respiratory airway, including bronchial epithelium, and in the female reproductive tract, including oviduct (at protein level). Detected in pancreatic intercalated ducts in the exocrine tissue, on epithelial cells in intralobular striated ducts in sublingual salivary glands, on apical membranes of crypt cells throughout the small and large intestine, and on the reabsorptive duct in eccrine sweat glands. Detected on the equatorial segment of the sperm head (at protein level). Detected in nasal and bronchial superficial epithelium. Expressed by the central cells on the sebaceous glands, dermal adipocytes and, at lower levels, by epithelial cells.
Binds and hydrolyzes ATP via the two cytoplasmic ABC transporter nucleotide-binding domains (PubMed:15284228). The two ATP-binding domains interact with each other, forming a head-to-tail dimer (PubMed:17036051). Normal ATPase activity requires interaction between the two domains (PubMed:15284228). The first ABC transporter nucleotide-binding domain has no ATPase activity by itself (By similarity).
The PDZ-binding motif mediates interactions with GOPC and with the SLC4A7, SLC9A3R1/EBP50 complex.
The R region is intrinsically disordered (PubMed:10792060, PubMed:17660831). It mediates channel activation when it is phosphorylated, but not in the absence of phosphorylation (PubMed:10792060).
Belongs to the ABC transporter superfamily. ABCC family. CFTR transporter (TC 3.A.1.202) subfamily.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Membrane transport > ABC transporters.
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Vibrio cholerae infection.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Gastric acid secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Pancreatic secretion.
文献引用
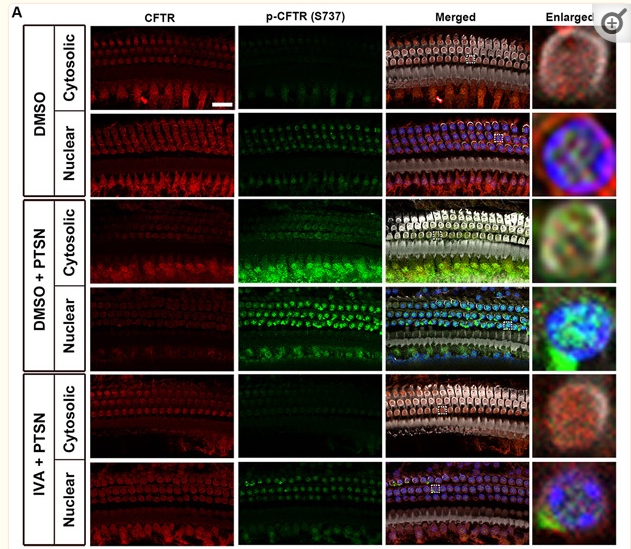
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
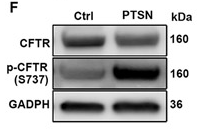
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.