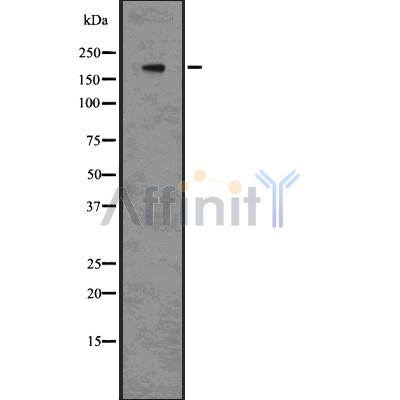
| 产品: | BRG1 抗体 |
| 货号: | DF7581 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to BRG1 |
| 应用: | WB IHC |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse |
| 预测: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| 分子量: | 185 kDa; 185kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | P51532 |
| RRID: | AB_2841072 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7581, RRID:AB_2841072.
展开/折叠
ATP dependent helicase SMARCA4; ATP-dependent helicase SMARCA4; BAF 190; BAF190; BAF190A; Brahma protein like 1; BRG1; BRG1 associated factor 190A; BRG1 protein; BRG1-associated factor 190A; BRM/SWI2 related gene 1; Global transcription activator homologous sequence; global transcription activator snf2l4; Homeotic gene regulator; hSNF2b; Mitotic growth and transcription activator; MRD16; Nuclear protein GRB1; Protein brahma homolog 1; Protein BRG-1; Protein BRG1; RTPS2; SMARC A4; SMARCA4; SMCA4_HUMAN; SNF2; SNF2 beta; SNF2 like 4; SNF2-beta; SNF2B; SNF2L4; SNF2LB; Sucrose nonfermenting like 4; SWI/SNF related matrix associated actin dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 4; SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4; SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 4; SWI2; Transcription activator BRG1;
抗原和靶标
Colocalizes with ZEB1 in E-cadherin-negative cells from established lines, and stroma of normal colon as well as in de-differentiated epithelial cells at the invasion front of colorectal carcinomas (at protein level).
- P51532 SMCA4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSTPDPPLGGTPRPGPSPGPGPSPGAMLGPSPGPSPGSAHSMMGPSPGPPSAGHPIPTQGPGGYPQDNMHQMHKPMESMHEKGMSDDPRYNQMKGMGMRSGGHAGMGPPPSPMDQHSQGYPSPLGGSEHASSPVPASGPSSGPQMSSGPGGAPLDGADPQALGQQNRGPTPFNQNQLHQLRAQIMAYKMLARGQPLPDHLQMAVQGKRPMPGMQQQMPTLPPPSVSATGPGPGPGPGPGPGPGPAPPNYSRPHGMGGPNMPPPGPSGVPPGMPGQPPGGPPKPWPEGPMANAAAPTSTPQKLIPPQPTGRPSPAPPAVPPAASPVMPPQTQSPGQPAQPAPMVPLHQKQSRITPIQKPRGLDPVEILQEREYRLQARIAHRIQELENLPGSLAGDLRTKATIELKALRLLNFQRQLRQEVVVCMRRDTALETALNAKAYKRSKRQSLREARITEKLEKQQKIEQERKRRQKHQEYLNSILQHAKDFKEYHRSVTGKIQKLTKAVATYHANTEREQKKENERIEKERMRRLMAEDEEGYRKLIDQKKDKRLAYLLQQTDEYVANLTELVRQHKAAQVAKEKKKKKKKKKAENAEGQTPAIGPDGEPLDETSQMSDLPVKVIHVESGKILTGTDAPKAGQLEAWLEMNPGYEVAPRSDSEESGSEEEEEEEEEEQPQAAQPPTLPVEEKKKIPDPDSDDVSEVDARHIIENAKQDVDDEYGVSQALARGLQSYYAVAHAVTERVDKQSALMVNGVLKQYQIKGLEWLVSLYNNNLNGILADEMGLGKTIQTIALITYLMEHKRINGPFLIIVPLSTLSNWAYEFDKWAPSVVKVSYKGSPAARRAFVPQLRSGKFNVLLTTYEYIIKDKHILAKIRWKYMIVDEGHRMKNHHCKLTQVLNTHYVAPRRLLLTGTPLQNKLPELWALLNFLLPTIFKSCSTFEQWFNAPFAMTGEKVDLNEEETILIIRRLHKVLRPFLLRRLKKEVEAQLPEKVEYVIKCDMSALQRVLYRHMQAKGVLLTDGSEKDKKGKGGTKTLMNTIMQLRKICNHPYMFQHIEESFSEHLGFTGGIVQGLDLYRASGKFELLDRILPKLRATNHKVLLFCQMTSLMTIMEDYFAYRGFKYLRLDGTTKAEDRGMLLKTFNEPGSEYFIFLLSTRAGGLGLNLQSADTVIIFDSDWNPHQDLQAQDRAHRIGQQNEVRVLRLCTVNSVEEKILAAAKYKLNVDQKVIQAGMFDQKSSSHERRAFLQAILEHEEQDESRHCSTGSGSASFAHTAPPPAGVNPDLEEPPLKEEDEVPDDETVNQMIARHEEEFDLFMRMDLDRRREEARNPKRKPRLMEEDELPSWIIKDDAEVERLTCEEEEEKMFGRGSRHRKEVDYSDSLTEKQWLKAIEEGTLEEIEEEVRQKKSSRKRKRDSDAGSSTPTTSTRSRDKDDESKKQKKRGRPPAEKLSPNPPNLTKKMKKIVDAVIKYKDSSSGRQLSEVFIQLPSRKELPEYYELIRKPVDFKKIKERIRNHKYRSLNDLEKDVMLLCQNAQTFNLEGSLIYEDSIVLQSVFTSVRQKIEKEDDSEGEESEEEEEGEEEGSESESRSVKVKIKLGRKEKAQDRLKGGRRRPSRGSRAKPVVSDDDSEEEQEEDRSGSGSEED
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
翻译修饰 - P51532 作为底物
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| T3 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T11 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S31 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S35 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R181 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K188 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| R192 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K207 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T298 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S323 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T353 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K357 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K399 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K405 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K437 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K437 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S446 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K455 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K455 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K461 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K471 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K487 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K496 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K502 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| R529 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| Y538 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T596 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T609 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S610 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S613 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S624 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K626 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K626 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S660 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S662 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T681 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K689 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S695 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S699 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K711 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y718 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S721 | Phosphorylation | Q13315 (ATM) | Uniprot |
| Y732 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K831 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K835 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S837 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S850 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K872 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K991 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K997 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1014 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1033 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1081 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| R1087 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| Y1123 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1131 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1213 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1219 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1219 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y1220 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1221 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1227 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K1227 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1237 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1291 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| S1345 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1349 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K1349 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T1358 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1365 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S1371 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1375 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y1379 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1380 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1382 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1386 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T1396 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1410 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1417 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1421 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1422 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1423 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1425 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1426 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1428 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1452 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1459 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1492 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y1497 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1570 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1575 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1586 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1592 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1627 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1631 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1640 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1642 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1644 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot |
研究背景
Involved in transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling (alteration of DNA-nucleosome topology). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes that carry out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Component of the CREST-BRG1 complex, a multiprotein complex that regulates promoter activation by orchestrating the calcium-dependent release of a repressor complex and the recruitment of an activator complex. In resting neurons, transcription of the c-FOS promoter is inhibited by SMARCA4-dependent recruitment of a phospho-RB1-HDAC repressor complex. Upon calcium influx, RB1 is dephosphorylated by calcineurin, which leads to release of the repressor complex. At the same time, there is increased recruitment of CREBBP to the promoter by a CREST-dependent mechanism, which leads to transcriptional activation. The CREST-BRG1 complex also binds to the NR2B promoter, and activity-dependent induction of NR2B expression involves the release of HDAC1 and recruitment of CREBBP. Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development, a switch from a stem/progenitor to a postmitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to postmitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth. SMARCA4/BAF190A may promote neural stem cell self-renewal/proliferation by enhancing Notch-dependent proliferative signals, while concurrently making the neural stem cell insensitive to SHH-dependent differentiating cues (By similarity). Acts as a corepressor of ZEB1 to regulate E-cadherin transcription and is required for induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by ZEB1. Binds via DLX1 to enhancers located in the intergenic region between DLX5 and DLX6 and this binding is stabilized by the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) Evf2 (By similarity). Binds to RNA in a promiscuous manner (By similarity). Binding to RNAs including lncRNA Evf2 leads to inhibition of SMARCA4 ATPase and chromatin remodeling activities (By similarity).
Nucleus.
Note: Colocalizes with long non-coding RNA Evf2 in nuclear RNA clouds.
Colocalizes with ZEB1 in E-cadherin-negative cells from established lines, and stroma of normal colon as well as in de-differentiated epithelial cells at the invasion front of colorectal carcinomas (at protein level).
Component of the multiprotein chromatin-remodeling complexes SWI/SNF: SWI/SNF-A (BAF), SWI/SNF-B (PBAF) and related complexes. The canonical complex contains a catalytic subunit (either SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A or SMARCA2/BRM/BAF190B) and at least SMARCE1, ACTL6A/BAF53, SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCC2/BAF170, and SMARCB1/SNF5/BAF47. Other subunits specific to each of the complexes may also be present permitting several possible developmental- and tissue-specific combinations. Component of the BAF complex, which includes at least actin (ACTB), ARID1A/BAF250A, ARID1B/BAF250B, SMARCA2/BRM, SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A, ACTL6A/BAF53, ACTL6B/BAF53B, SMARCE1/BAF57, SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCC2/BAF170, SMARCB1/SNF5/INI1, and one or more SMARCD1/BAF60A, SMARCD2/BAF60B, or SMARCD3/BAF60C. In muscle cells, the BAF complex also contains DPF3. Component of neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) composed of at least, ARID1A/BAF250A or ARID1B/BAF250B, SMARCD1/BAF60A, SMARCD3/BAF60C, SMARCA2/BRM/BAF190B, SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A, SMARCB1/BAF47, SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCE1/BAF57, SMARCC2/BAF170, PHF10/BAF45A, ACTL6A/BAF53A and actin. Component of neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex) composed of at least, ARID1A/BAF250A or ARID1B/BAF250B, SMARCD1/BAF60A, SMARCD3/BAF60C, SMARCA2/BRM/BAF190B, SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A, SMARCB1/BAF47, SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCE1/BAF57, SMARCC2/BAF170, DPF1/BAF45B, DPF3/BAF45C, ACTL6B/BAF53B and actin. Component of the SWI/SNF-B (PBAF) chromatin remodeling complex, at least composed of SMARCA4/BRG1, SMARCB1/BAF47/SNF5, ACTL6A/BAF53A or ACTL6B/BAF53B, SMARCE1/BAF57, SMARCD1/BAF60A, SMARCD2/BAF60B, perhaps SMARCD3/BAF60C, SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCC2/BAF170, PBRM1/BAF180, ARID2/BAF200 and actin. Component of SWI/SNF (GBAF) subcomplex, which includes at least BICRA or BICRAL (mutually exclusive), BRD9, SS18, SMARCA2/BRM, SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A, ACTL6A/BAF53, SMARCC1/BAF155, and SMARCD1/BAF60A. Component of the BAF53 complex, at least composed of BAF53A, RUVBL1, SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A, and TRRAP, which preferentially acetylates histone H4 (and H2A) within nucleosomes. Component of the CREST-BRG1 complex, at least composed of SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A, SS18L1/CREST, HDAC1, RB1 and SP1 (By similarity). Interacts with PHF10/BAF45A (By similarity). Interacts with MYOG (By similarity). Interacts directly with IKFZ1; the interaction associates IKFZ1 with the BAF complex. Interacts with ZEB1 (via N-terminus). Interacts with NR3C1, PGR, SMARD1, TOPBP1 and ZMIM2/ZIMP7. Interacts with (via the bromodomain) with TERT; the interaction regulates Wnt-mediated signaling. Interacts with TBX21 in a KDM6B-dependent manner (By similarity). Interacts with KDM6A and KDM6B (By similarity). Interacts with HNRNPU; this interaction occurs in embryonic stem cells and stimulates global Pol II-mediated transcription (By similarity). Interacts with ACTL6A. Interacts with DLX1 (By similarity). Interacts with DPF2.
Belongs to the SNF2/RAD54 helicase family.
研究领域
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.