| 产品: | GCN2 抗体 |
| 货号: | DF7801 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to GCN2 |
| 应用: | WB |
| 文献验证: | WB |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 预测: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| 分子量: | 190~230kDa; 187kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | Q9P2K8 |
| RRID: | AB_2841256 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7801, RRID:AB_2841256.
展开/折叠
E2AK4_HUMAN; Eif2ak4; Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 2 alpha kinase 4; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 4; GCN2; GCN2 eIF2alpha kinase; GCN2 like protein; GCN2-like protein; KIAA1338; MGCN2;
抗原和靶标
Widely expressed (PubMed:10504407). Expressed in lung, smooth muscle cells and macrophages (PubMed:24292273).
- Q9P2K8 E2AK4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAGGRGAPGRGRDEPPESYPQRQDHELQALEAIYGADFQDLRPDACGPVKEPPEINLVLYPQGLTGEEVYVKVDLRVKCPPTYPDVVPEIELKNAKGLSNESVNLLKSRLEELAKKHCGEVMIFELAYHVQSFLSEHNKPPPKSFHEEMLERRAQEEQQRLLEAKRKEEQEQREILHEIQRRKEEIKEEKKRKEMAKQERLEIASLSNQDHTSKKDPGGHRTAAILHGGSPDFVGNGKHRANSSGRSRRERQYSVCNSEDSPGSCEILYFNMGSPDQLMVHKGKCIGSDEQLGKLVYNALETATGGFVLLYEWVLQWQKKMGPFLTSQEKEKIDKCKKQIQGTETEFNSLVKLSHPNVVRYLAMNLKEQDDSIVVDILVEHISGVSLAAHLSHSGPIPVHQLRRYTAQLLSGLDYLHSNSVVHKVLSASNVLVDAEGTVKITDYSISKRLADICKEDVFEQTRVRFSDNALPYKTGKKGDVWRLGLLLLSLSQGQECGEYPVTIPSDLPADFQDFLKKCVCLDDKERWSPQQLLKHSFINPQPKMPLVEQSPEDSEGQDYVETVIPSNRLPSAAFFSETQRQFSRYFIEFEELQLLGKGAFGAVIKVQNKLDGCCYAVKRIPINPASRQFRRIKGEVTLLSRLHHENIVRYYNAWIERHERPAGPGTPPPDSGPLAKDDRAARGQPASDTDGLDSVEAAAPPPILSSSVEWSTSGERSASARFPATGPGSSDDEDDDEDEHGGVFSQSFLPASDSESDIIFDNEDENSKSQNQDEDCNEKNGCHESEPSVTTEAVHYLYIQMEYCEKSTLRDTIDQGLYRDTVRLWRLFREILDGLAYIHEKGMIHRDLKPVNIFLDSDDHVKIGDFGLATDHLAFSADSKQDDQTGDLIKSDPSGHLTGMVGTALYVSPEVQGSTKSAYNQKVDLFSLGIIFFEMSYHPMVTASERIFVLNQLRDPTSPKFPEDFDDGEHAKQKSVISWLLNHDPAKRPTATELLKSELLPPPQMEESELHEVLHHTLTNVDGKAYRTMMAQIFSQRISPAIDYTYDSDILKGNFSIRTAKMQQHVCETIIRIFKRHGAVQLCTPLLLPRNRQIYEHNEAALFMDHSGMLVMLPFDLRIPFARYVARNNILNLKRYCIERVFRPRKLDRFHPKELLECAFDIVTSTTNSFLPTAEIIYTIYEIIQEFPALQERNYSIYLNHTMLLKAILLHCGIPEDKLSQVYIILYDAVTEKLTRREVEAKFCNLSLSSNSLCRLYKFIEQKGDLQDLMPTINSLIKQKTGIAQLVKYGLKDLEEVVGLLKKLGIKLQVLINLGLVYKVQQHNGIIFQFVAFIKRRQRAVPEILAAGGRYDLLIPQFRGPQALGPVPTAIGVSIAIDKISAAVLNMEESVTISSCDLLVVSVGQMSMSRAINLTQKLWTAGITAEIMYDWSQSQEELQEYCRHHEITYVALVSDKEGSHVKVKSFEKERQTEKRVLETELVDHVLQKLRTKVTDERNGREASDNLAVQNLKGSFSNASGLFEIHGATVVPIVSVLAPEKLSASTRRRYETQVQTRLQTSLANLHQKSSEIEILAVDLPKETILQFLSLEWDADEQAFNTTVKQLLSRLPKQRYLKLVCDEIYNIKVEKKVSVLFLYSYRDDYYRILF
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Metabolic-stress sensing protein kinase that phosphorylates the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF-2-alpha/EIF2S1) on 'Ser-52' in response to low amino acid availability. Plays a role as an activator of the integrated stress response (ISR) required for adapatation to amino acid starvation. Converts phosphorylated eIF-2-alpha/EIF2S1 either to a competitive inhibitor of the translation initiation factor eIF-2B, leading to a global protein synthesis repression, and thus to a reduced overall utilization of amino acids, or to a translational initiation activation of specific mRNAs, such as the transcriptional activator ATF4, and hence allowing ATF4-mediated reprogramming of amino acid biosynthetic gene expression to alleviate nutrient depletion. Binds uncharged tRNAs (By similarity). Involved in cell cycle arrest by promoting cyclin D1 mRNA translation repression after the unfolded protein response pathway (UPR) activation or cell cycle inhibitor CDKN1A/p21 mRNA translation activation in response to amino acid deprivation. Plays a role in the consolidation of synaptic plasticity, learning as well as formation of long-term memory. Plays a role in neurite outgrowth inhibition. Plays a proapoptotic role in response to glucose deprivation. Promotes global cellular protein synthesis repression in response to UV irradiation independently of the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK) and p38 MAPK signaling pathways (By similarity). Plays a role in the antiviral response against alphavirus infection; impairs early viral mRNA translation of the incoming genomic virus RNA, thus preventing alphavirus replication (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Plays a role in modulating the adaptive immune response to yellow fever virus infection; promotes dendritic cells to initiate autophagy and antigene presentation to both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cells under amino acid starvation.
Autophosphorylated; autophosphorylation on Thr-899 is increased upon amino acid starvation and in UV irradiation cells and inhibited in presence of IMPACT.
Cytoplasm.
Widely expressed. Expressed in lung, smooth muscle cells and macrophages.
Homodimer; homodimerization is important for kinase activation by uncharged tRNAs. Interacts with GCN1; this interaction stimulates EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity and is impaired by IMPACT upon a variety of stress conditions, such as amino acid depletion, UV-C irradiation, proteasome inhibitor treatment and glucose deprivation. Interacts with DNAJC3; this interaction inhibits EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity during endoplasmic reticulum (ER), hypothermic and amino acid-starving stress conditions.
The histidyl-tRNA synthetase-like region and protein kinase domains are necessary for eIF-2-alpha kinase activity and eIF-2-alpha-mediated translational control. The histidyl-tRNA synthetase-like domain is necessary for binding to uncharged tRNAs. Kinase domain 1 is a degenerate kinase domain.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. GCN2 subfamily.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
文献引用
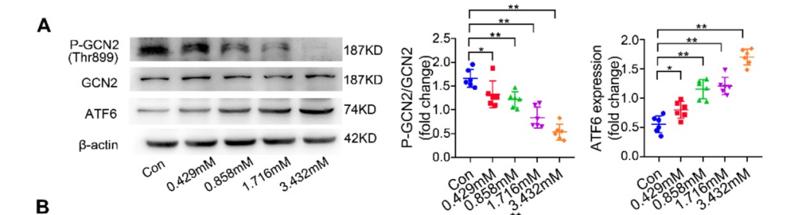
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: Heart
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.