| 产品: | PDCD6IP 抗体 |
| 货号: | DF9027 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to PDCD6IP |
| 应用: | WB |
| 文献验证: | WB |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 预测: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| 分子量: | 96 kDa; 96kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | Q8WUM4 |
| RRID: | AB_2842223 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF9027, RRID:AB_2842223.
展开/折叠
AIP1; ALG 2 interacting protein 1; ALG-2-interacting protein 1; ALG2 interacting protein X; Alix; Apoptosis linked gene 2 interacting protein X; Dopamine receptor interacting protein 4; DRIP4; Hp95; KIAA1375; MGC17003; PDC6I_HUMAN; PDCD6 interacting protein; PDCD6-interacting protein; PDCD6IP; Programmed cell death 6 interacting protein; Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein;
抗原和靶标
- Q8WUM4 PDC6I_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MATFISVQLKKTSEVDLAKPLVKFIQQTYPSGGEEQAQYCRAAEELSKLRRAAVGRPLDKHEGALETLLRYYDQICSIEPKFPFSENQICLTFTWKDAFDKGSLFGGSVKLALASLGYEKSCVLFNCAALASQIAAEQNLDNDEGLKIAAKHYQFASGAFLHIKETVLSALSREPTVDISPDTVGTLSLIMLAQAQEVFFLKATRDKMKDAIIAKLANQAADYFGDAFKQCQYKDTLPKEVFPVLAAKHCIMQANAEYHQSILAKQQKKFGEEIARLQHAAELIKTVASRYDEYVNVKDFSDKINRALAAAKKDNDFIYHDRVPDLKDLDPIGKATLVKSTPVNVPISQKFTDLFEKMVPVSVQQSLAAYNQRKADLVNRSIAQMREATTLANGVLASLNLPAAIEDVSGDTVPQSILTKSRSVIEQGGIQTVDQLIKELPELLQRNREILDESLRLLDEEEATDNDLRAKFKERWQRTPSNELYKPLRAEGTNFRTVLDKAVQADGQVKECYQSHRDTIVLLCKPEPELNAAIPSANPAKTMQGSEVVNVLKSLLSNLDEVKKEREGLENDLKSVNFDMTSKFLTALAQDGVINEEALSVTELDRVYGGLTTKVQESLKKQEGLLKNIQVSHQEFSKMKQSNNEANLREEVLKNLATAYDNFVELVANLKEGTKFYNELTEILVRFQNKCSDIVFARKTERDELLKDLQQSIAREPSAPSIPTPAYQSSPAGGHAPTPPTPAPRTMPPTKPQPPARPPPPVLPANRAPSATAPSPVGAGTAAPAPSQTPGSAPPPQAQGPPYPTYPGYPGYCQMPMPMGYNPYAYGQYNMPYPPVYHQSPGQAPYPGPQQPSYPFPQPPQQSYYPQQ
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Multifunctional protein involved in endocytosis, multivesicular body biogenesis, membrane repair, cytokinesis, apoptosis and maintenance of tight junction integrity. Class E VPS protein involved in concentration and sorting of cargo proteins of the multivesicular body (MVB) for incorporation into intralumenal vesicles (ILVs) that are generated by invagination and scission from the limiting membrane of the endosome. Binds to the phospholipid lysobisphosphatidic acid (LBPA) which is abundant in MVBs internal membranes. The MVB pathway requires the sequential function of ESCRT-O, -I,-II and -III complexes. The ESCRT machinery also functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, such as the terminal stages of cytokinesis. Adapter for a subset of ESCRT-III proteins, such as CHMP4, to function at distinct membranes. Required for completion of cytokinesis. May play a role in the regulation of both apoptosis and cell proliferation. Regulates exosome biogenesis in concert with SDC1/4 and SDCBP. By interacting with F-actin, PARD3 and TJP1 secures the proper assembly and positioning of actomyosin-tight junction complex at the apical sides of adjacent epithelial cells that defines a spatial membrane domain essential for the maintenance of epithelial cell polarity and barrier (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Involved in HIV-1 virus budding. Can replace TSG101 it its role of supporting HIV-1 release; this function requires the interaction with CHMP4B. The ESCRT machinery also functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, such as enveloped virus budding (HIV-1 and other lentiviruses).
May be phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by activated PDGFRB.
Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Melanosome. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Secreted>Extracellular exosome. Cell junction>Tight junction. Midbody>Midbody ring.
Note: Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV. Colocalized with CEP55 at centrosomes of non-dividing cells. Component of the actomyosin-tight junction complex (By similarity). PDCD6IP targeting to the midbody requires the interaction with CEP55 (PubMed:18641129).
Self-associates. Interacts with SH3KBP1/CIN85 (By similarity). Interacts with PDCD6 in a calcium -dependent manner. Interacts with TSG101 in a calcium-dependent manner; PDCD6IP homooligomerization may be required for TSG101-binding. Interacts with SGSM3. Directly interacts with CHMP4A, CHMP4B and CHMP4C. Directly interacts with CEP55 in a 1:2 stoechiometry. The interaction with CEP55 is required for PDCD6IP targeting to the midbody. May interact with PDGFRB. Interacts with SH3GL1 and SH3GL2/endophilin-1. Forms a complex with SDCBP and SDC2. Found in a complex with F-actin, TJP1/ZO-1 and PARD3 (By similarity). Interacts with CD2AP. Interacts with ARRDC1.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 p6. Interacts with HIV-1 p9.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with EIAV p9.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Murine leukemia virus Gag polyprotein (via LYPX(n)L motif).
(Microbial infection) Interacts with ebola virus protein VP40 (via YPx(n)L/I motif).
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
文献引用
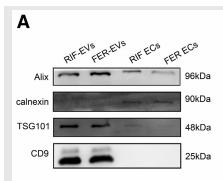
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: RIF-EVs and FER-EVs.
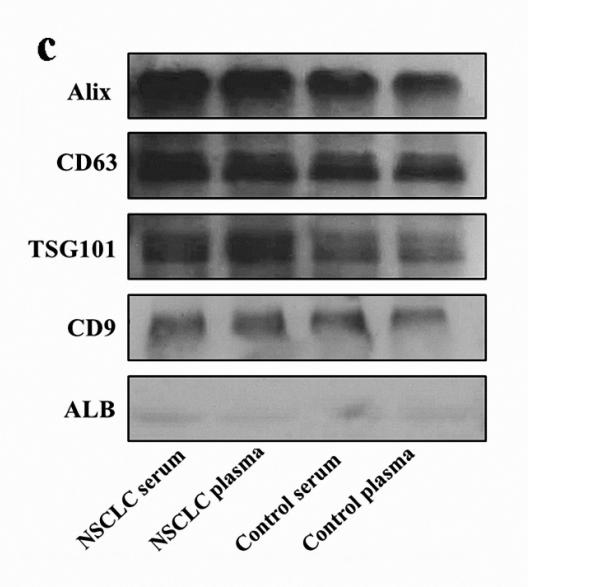
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: lung tissues
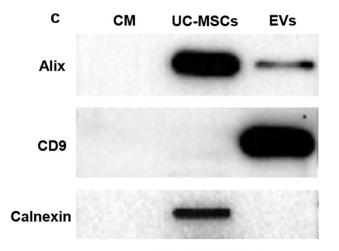
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: granulosa cells
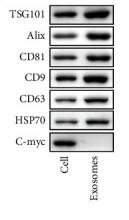
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.