产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF12084, RRID:AB_2844889.
展开/折叠
H1RNA; MGC108918; Ribonuclease H type II; RibonucleaseH1; RNaseH1; RNH1;
抗原和靶标
- O60930 RNH1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSWLLFLAHRVALAALPCRRGSRGFGMFYAVRRGRKTGVFLTWNECRAQVDRFPAARFKKFATEDEAWAFVRKSASPEVSEGHENQHGQESEAKASKRLREPLDGDGHESAEPYAKHMKPSVEPAPPVSRDTFSYMGDFVVVYTDGCCSSNGRRRPRAGIGVYWGPGHPLNVGIRLPGRQTNQRAEIHAACKAIEQAKTQNINKLVLYTDSMFTINGITNWVQGWKKNGWKTSAGKEVINKEDFVALERLTQGMDIQWMHVPGHSGFIGNEEADRLAREGAKQSED
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Endonuclease that specifically degrades the RNA of RNA-DNA hybrids. Plays a role in RNA polymerase II (RNAp II) transcription termination by degrading R-loop RNA-DNA hybrid formation at G-rich pause sites located downstream of the poly(A) site and behind the elongating RNAp II.
Cytoplasm.
Ubiquitous.
Monomer.
Belongs to the RNase H family.
研究领域
· Genetic Information Processing > Replication and repair > DNA replication.
文献引用
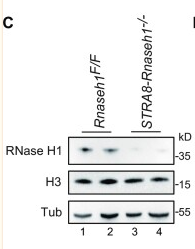
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.