| 产品: | 磷酸化 CDK5 (Tyr239) 抗体 |
| 货号: | AF3628 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-CDK5 (Tyr239) |
| 应用: | IHC |
| 文献验证: | IHC |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 分子量: | 33kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | Q00535 |
| RRID: | AB_2846942 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3628, RRID:AB_2846942.
展开/折叠
Cdk 5; Cdk5; CDK5_HUMAN; Cell division protein kinase 5; Crk6; Cyclin dependent kinase 5; Cyclin-dependent kinase 5; Protein kinase CDK5 splicing; PSSALRE; Serine threonine protein kinase PSSALRE; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PSSALRE; Tau protein kinase II catalytic subunit; TPKII catalytic subunit;
抗原和靶标
A synthesized peptide derived from human CDK5 around the phosphorylation site of Tyr239.
Isoform 1 is ubiquitously expressed. Accumulates in cortical neurons (at protein level). Isoform 2 has only been detected in testis, skeletal muscle, colon, bone marrow and ovary.
- Q00535 CDK5_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MQKYEKLEKIGEGTYGTVFKAKNRETHEIVALKRVRLDDDDEGVPSSALREICLLKELKHKNIVRLHDVLHSDKKLTLVFEFCDQDLKKYFDSCNGDLDPEIVKSFLFQLLKGLGFCHSRNVLHRDLKPQNLLINRNGELKLADFGLARAFGIPVRCYSAEVVTLWYRPPDVLFGAKLYSTSIDMWSAGCIFAELANAGRPLFPGNDVDDQLKRIFRLLGTPTEEQWPSMTKLPDYKPYPMYPATTSLVNVVPKLNATGRDLLQNLLKCNPVQRISAEEALQHPYFSDFCPP
研究背景
Proline-directed serine/threonine-protein kinase essential for neuronal cell cycle arrest and differentiation and may be involved in apoptotic cell death in neuronal diseases by triggering abortive cell cycle re-entry. Interacts with D1 and D3-type G1 cyclins. Phosphorylates SRC, NOS3, VIM/vimentin, p35/CDK5R1, MEF2A, SIPA1L1, SH3GLB1, PXN, PAK1, MCAM/MUC18, SEPT5, SYN1, DNM1, AMPH, SYNJ1, CDK16, RAC1, RHOA, CDC42, TONEBP/NFAT5, MAPT/TAU, MAP1B, histone H1, p53/TP53, HDAC1, APEX1, PTK2/FAK1, huntingtin/HTT, ATM, MAP2, NEFH and NEFM. Regulates several neuronal development and physiological processes including neuronal survival, migration and differentiation, axonal and neurite growth, synaptogenesis, oligodendrocyte differentiation, synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission, by phosphorylating key proteins. Activated by interaction with CDK5R1 (p35) and CDK5R2 (p39), especially in post-mitotic neurons, and promotes CDK5R1 (p35) expression in an autostimulation loop. Phosphorylates many downstream substrates such as Rho and Ras family small GTPases (e.g. PAK1, RAC1, RHOA, CDC42) or microtubule-binding proteins (e.g. MAPT/TAU, MAP2, MAP1B), and modulates actin dynamics to regulate neurite growth and/or spine morphogenesis. Phosphorylates also exocytosis associated proteins such as MCAM/MUC18, SEPT5, SYN1, and CDK16/PCTAIRE1 as well as endocytosis associated proteins such as DNM1, AMPH and SYNJ1 at synaptic terminals. In the mature central nervous system (CNS), regulates neurotransmitter movements by phosphorylating substrates associated with neurotransmitter release and synapse plasticity; synaptic vesicle exocytosis, vesicles fusion with the presynaptic membrane, and endocytosis. Promotes cell survival by activating anti-apoptotic proteins BCL2 and STAT3, and negatively regulating of JNK3/MAPK10 activity. Phosphorylation of p53/TP53 in response to genotoxic and oxidative stresses enhances its stabilization by preventing ubiquitin ligase-mediated proteasomal degradation, and induces transactivation of p53/TP53 target genes, thus regulating apoptosis. Phosphorylation of p35/CDK5R1 enhances its stabilization by preventing calpain-mediated proteolysis producing p25/CDK5R1 and avoiding ubiquitin ligase-mediated proteasomal degradation. During aberrant cell-cycle activity and DNA damage, p25/CDK5 activity elicits cell-cycle activity and double-strand DNA breaks that precedes neuronal death by deregulating HDAC1. DNA damage triggered phosphorylation of huntingtin/HTT in nuclei of neurons protects neurons against polyglutamine expansion as well as DNA damage mediated toxicity. Phosphorylation of PXN reduces its interaction with PTK2/FAK1 in matrix-cell focal adhesions (MCFA) during oligodendrocytes (OLs) differentiation. Negative regulator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Activator of the GAIT (IFN-gamma-activated inhibitor of translation) pathway, which suppresses expression of a post-transcriptional regulon of proinflammatory genes in myeloid cells; phosphorylates the linker domain of glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase (EPRS) in a IFN-gamma-dependent manner, the initial event in assembly of the GAIT complex. Phosphorylation of SH3GLB1 is required for autophagy induction in starved neurons. Phosphorylation of TONEBP/NFAT5 in response to osmotic stress mediates its rapid nuclear localization. MEF2 is inactivated by phosphorylation in nucleus in response to neurotoxin, thus leading to neuronal apoptosis. APEX1 AP-endodeoxyribonuclease is repressed by phosphorylation, resulting in accumulation of DNA damage and contributing to neuronal death. NOS3 phosphorylation down regulates NOS3-derived nitrite (NO) levels. SRC phosphorylation mediates its ubiquitin-dependent degradation and thus leads to cytoskeletal reorganization. May regulate endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis via the modulation of lamellipodia formation. Involved in dendritic spine morphogenesis by mediating the EFNA1-EPHA4 signaling. The complex p35/CDK5 participates in the regulation of the circadian clock by modulating the function of CLOCK protein: phosphorylates CLOCK at 'Thr-451' and 'Thr-461' and regulates the transcriptional activity of the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer in association with altered stability and subcellular distribution.
Phosphorylation on Tyr-15 by ABL1 and FYN, and on Ser-159 by casein kinase 1 promotes kinase activity. By contrast, phosphorylation at Thr-14 inhibits activity.
Phosphorylation at Ser-159 is essential for maximal catalytic activity.
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Perikaryon. Cell projection>Lamellipodium. Cell projection>Growth cone. Cell junction>Synapse>Postsynaptic density.
Note: In axonal growth cone with extension to the peripheral lamellipodia (By similarity). Under neurotoxic stress and neuronal injury conditions, CDK5R (p35) is cleaved by calpain to generate CDK5R1 (p25) in response to increased intracellular calcium. The elevated level of p25, when in complex with CDK5, leads to its subcellular misallocation as well as its hyperactivation. Colocalizes with CTNND2 in the cell body of neuronal cells, and with CTNNB1 in the cell-cell contacts and plasma membrane of undifferentiated and differentiated neuroblastoma cells. Reversibly attached to the plasma membrane in an inactive form when complexed to dephosphorylated p35 or CDK5R2 (p39), p35 phosphorylation releases this attachment and activates CDK5.
Nucleus.
Isoform 1 is ubiquitously expressed. Accumulates in cortical neurons (at protein level). Isoform 2 has only been detected in testis, skeletal muscle, colon, bone marrow and ovary.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CDC2/CDKX subfamily.
研究领域
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Cocaine addiction.
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
文献引用
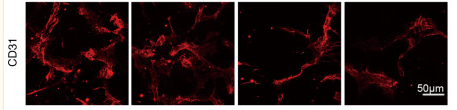
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
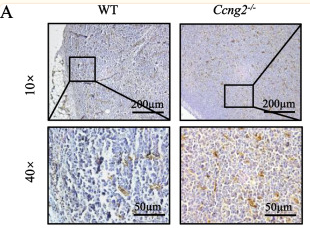
Application: IHC Species: Mouse Sample:
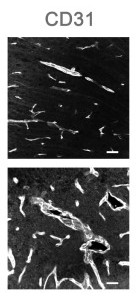
Application: IHC Species: Mouse Sample: brain tissue
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: HCC cell
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.