产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6226, RRID:AB_2835100.
展开/折叠
70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1; KS6B1_HUMAN; p70 alpha; P70 beta 1; p70 ribosomal S6 kinase alpha; p70 ribosomal S6 kinase beta 1; p70 S6 kinase alpha; P70 S6 Kinase; p70 S6 kinase, alpha 1; p70 S6 kinase, alpha 2; p70 S6K; p70 S6K-alpha; p70 S6KA; p70(S6K) alpha; p70(S6K)-alpha; p70-alpha; p70-S6K 1; p70-S6K; P70S6K; P70S6K1; p70S6Kb; PS6K; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 70kDa polypeptide 1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta 1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase I; RPS6KB1; S6K; S6K-beta-1; S6K1; Serine/threonine kinase 14 alpha; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 14A; STK14A;
抗原和靶标
- P23443 KS6B1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRRRRRRDGFYPAPDFRDREAEDMAGVFDIDLDQPEDAGSEDELEEGGQLNESMDHGGVGPYELGMEHCEKFEISETSVNRGPEKIRPECFELLRVLGKGGYGKVFQVRKVTGANTGKIFAMKVLKKAMIVRNAKDTAHTKAERNILEEVKHPFIVDLIYAFQTGGKLYLILEYLSGGELFMQLEREGIFMEDTACFYLAEISMALGHLHQKGIIYRDLKPENIMLNHQGHVKLTDFGLCKESIHDGTVTHTFCGTIEYMAPEILMRSGHNRAVDWWSLGALMYDMLTGAPPFTGENRKKTIDKILKCKLNLPPYLTQEARDLLKKLLKRNAASRLGAGPGDAGEVQAHPFFRHINWEELLARKVEPPFKPLLQSEEDVSQFDSKFTRQTPVDSPDDSTLSESANQVFLGFTYVAPSVLESVKEKFSFEPKIRSPRRFIGSPRTPVSPVKFSPGDFWGRGASASTANPQTPVEYPMETSGIEQMDVTMSGEASAPLPIRQPNSGPYKKQAFPMISKRPEHLRMNL
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts downstream of mTOR signaling in response to growth factors and nutrients to promote cell proliferation, cell growth and cell cycle progression. Regulates protein synthesis through phosphorylation of EIF4B, RPS6 and EEF2K, and contributes to cell survival by repressing the pro-apoptotic function of BAD. Under conditions of nutrient depletion, the inactive form associates with the EIF3 translation initiation complex. Upon mitogenic stimulation, phosphorylation by the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) leads to dissociation from the EIF3 complex and activation. The active form then phosphorylates and activates several substrates in the pre-initiation complex, including the EIF2B complex and the cap-binding complex component EIF4B. Also controls translation initiation by phosphorylating a negative regulator of EIF4A, PDCD4, targeting it for ubiquitination and subsequent proteolysis. Promotes initiation of the pioneer round of protein synthesis by phosphorylating POLDIP3/SKAR. In response to IGF1, activates translation elongation by phosphorylating EEF2 kinase (EEF2K), which leads to its inhibition and thus activation of EEF2. Also plays a role in feedback regulation of mTORC2 by mTORC1 by phosphorylating RICTOR, resulting in the inhibition of mTORC2 and AKT1 signaling. Mediates cell survival by phosphorylating the pro-apoptotic protein BAD and suppressing its pro-apoptotic function. Phosphorylates mitochondrial URI1 leading to dissociation of a URI1-PPP1CC complex. The free mitochondrial PPP1CC can then dephosphorylate RPS6KB1 at Thr-412, which is proposed to be a negative feedback mechanism for the RPS6KB1 anti-apoptotic function. Mediates TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance by phosphorylating IRS1 at multiple serine residues, resulting in accelerated degradation of IRS1. In cells lacking functional TSC1-2 complex, constitutively phosphorylates and inhibits GSK3B. May be involved in cytoskeletal rearrangement through binding to neurabin. Phosphorylates and activates the pyrimidine biosynthesis enzyme CAD, downstream of MTOR. Following activation by mTORC1, phosphorylates EPRS and thereby plays a key role in fatty acid uptake by adipocytes and also most probably in interferon-gamma-induced translation inhibition.
Phosphorylation at Thr-412 is regulated by mTORC1. The phosphorylation at this site is maintained by an agonist-dependent autophosphorylation mechanism (By similarity). Activated by phosphorylation at Thr-252 by PDPK1. Dephosphorylation by PPP1CC at Thr-412 in mitochondrion.
Cell junction>Synapse>Synaptosome. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Mitochondrion.
Note: Colocalizes with URI1 at mitochondrion.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm.
Widely expressed.
Interacts with PPP1R9A/neurabin-1 (By similarity). Interacts with RPTOR. Interacts with IRS1. Interacts with EIF3B and EIF3C. Interacts with TRAF4. Interacts with POLDIP3. Interacts (via N-terminus) with IER5.
The autoinhibitory domain is believed to block phosphorylation within the AGC-kinase C-terminal domain and the activation loop.
The TOS (TOR signaling) motif is essential for activation by mTORC1.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. S6 kinase subfamily.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > mTOR signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
文献引用
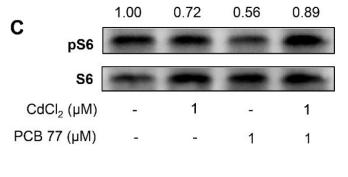
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HEL cells
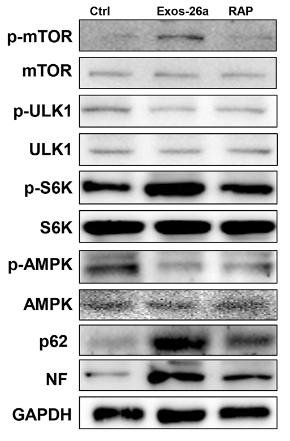
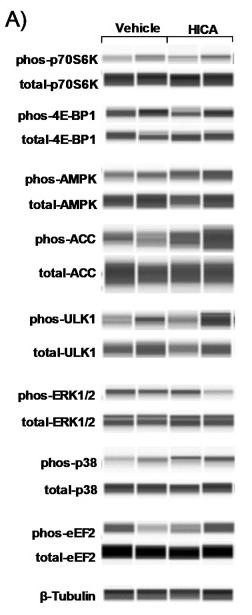
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: CRC cells
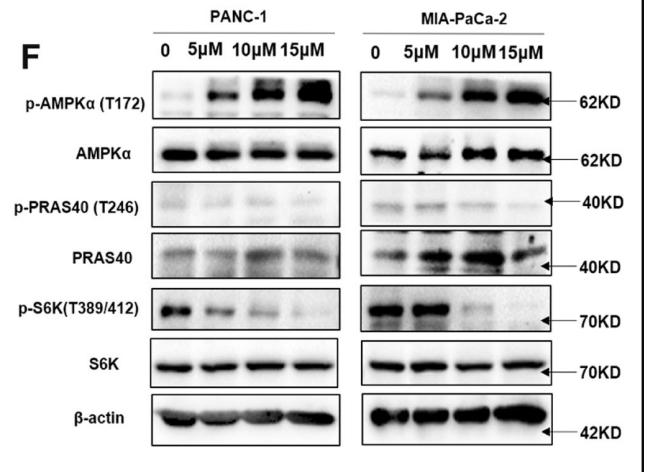
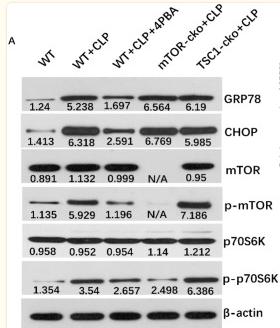
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: pancreatic cancer tissue
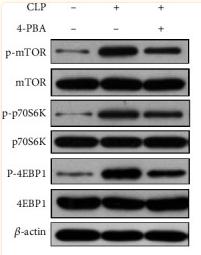
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: PC16 cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: osteoblasts
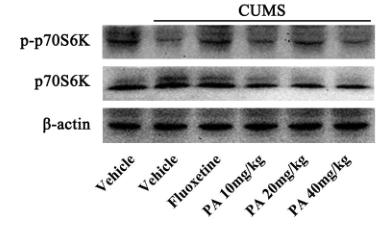
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: hippocampus
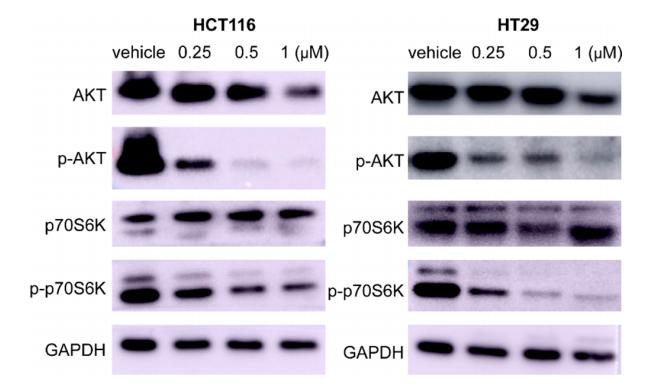
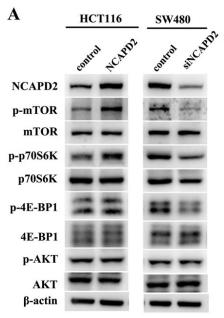
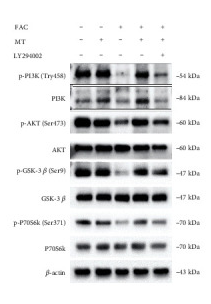
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HCT116 and HT-29 cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: Hep-G2 cells
Application: WB Species: fish Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.