产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6281, RRID:AB_2835132.
展开/折叠
CD309; CD309 antigen; EC 2.7.10.1; Fetal liver kinase 1; FLK-1; FLK1; FLK1, mouse, homolog of; Kdr; Kinase insert domain receptor (a type III receptor tyrosine kinase); Kinase insert domain receptor; KRD1; Ly73; Protein tyrosine kinase receptor FLK1; Protein-tyrosine kinase receptor flk-1; soluble VEGFR2; Tyrosine kinase growth factor receptor; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; VEGFR 2; VEGFR; VEGFR-2; VEGFR2; VGFR2_HUMAN;
抗原和靶标
- P35968 VGFR2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MQSKVLLAVALWLCVETRAASVGLPSVSLDLPRLSIQKDILTIKANTTLQITCRGQRDLDWLWPNNQSGSEQRVEVTECSDGLFCKTLTIPKVIGNDTGAYKCFYRETDLASVIYVYVQDYRSPFIASVSDQHGVVYITENKNKTVVIPCLGSISNLNVSLCARYPEKRFVPDGNRISWDSKKGFTIPSYMISYAGMVFCEAKINDESYQSIMYIVVVVGYRIYDVVLSPSHGIELSVGEKLVLNCTARTELNVGIDFNWEYPSSKHQHKKLVNRDLKTQSGSEMKKFLSTLTIDGVTRSDQGLYTCAASSGLMTKKNSTFVRVHEKPFVAFGSGMESLVEATVGERVRIPAKYLGYPPPEIKWYKNGIPLESNHTIKAGHVLTIMEVSERDTGNYTVILTNPISKEKQSHVVSLVVYVPPQIGEKSLISPVDSYQYGTTQTLTCTVYAIPPPHHIHWYWQLEEECANEPSQAVSVTNPYPCEEWRSVEDFQGGNKIEVNKNQFALIEGKNKTVSTLVIQAANVSALYKCEAVNKVGRGERVISFHVTRGPEITLQPDMQPTEQESVSLWCTADRSTFENLTWYKLGPQPLPIHVGELPTPVCKNLDTLWKLNATMFSNSTNDILIMELKNASLQDQGDYVCLAQDRKTKKRHCVVRQLTVLERVAPTITGNLENQTTSIGESIEVSCTASGNPPPQIMWFKDNETLVEDSGIVLKDGNRNLTIRRVRKEDEGLYTCQACSVLGCAKVEAFFIIEGAQEKTNLEIIILVGTAVIAMFFWLLLVIILRTVKRANGGELKTGYLSIVMDPDELPLDEHCERLPYDASKWEFPRDRLKLGKPLGRGAFGQVIEADAFGIDKTATCRTVAVKMLKEGATHSEHRALMSELKILIHIGHHLNVVNLLGACTKPGGPLMVIVEFCKFGNLSTYLRSKRNEFVPYKTKGARFRQGKDYVGAIPVDLKRRLDSITSSQSSASSGFVEEKSLSDVEEEEAPEDLYKDFLTLEHLICYSFQVAKGMEFLASRKCIHRDLAARNILLSEKNVVKICDFGLARDIYKDPDYVRKGDARLPLKWMAPETIFDRVYTIQSDVWSFGVLLWEIFSLGASPYPGVKIDEEFCRRLKEGTRMRAPDYTTPEMYQTMLDCWHGEPSQRPTFSELVEHLGNLLQANAQQDGKDYIVLPISETLSMEEDSGLSLPTSPVSCMEEEEVCDPKFHYDNTAGISQYLQNSKRKSRPVSVKTFEDIPLEEPEVKVIPDDNQTDSGMVLASEELKTLEDRTKLSPSFGGMVPSKSRESVASEGSNQTSGYQSGYHSDDTDTTVYSSEEAELLKLIEIGVQTGSTAQILQPDSGTTLSSPPV
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC and VEGFD. Plays an essential role in the regulation of angiogenesis, vascular development, vascular permeability, and embryonic hematopoiesis. Promotes proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation of endothelial cells. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Isoforms lacking a transmembrane domain, such as isoform 2 and isoform 3, may function as decoy receptors for VEGFA, VEGFC and/or VEGFD. Isoform 2 plays an important role as negative regulator of VEGFA- and VEGFC-mediated lymphangiogenesis by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and/or VEGFC and preventing their binding to FLT4. Modulates FLT1 and FLT4 signaling by forming heterodimers. Binding of vascular growth factors to isoform 1 leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and activation of PTK2/FAK1. Required for VEGFA-mediated induction of NOS2 and NOS3, leading to the production of the signaling molecule nitric oxide (NO) by endothelial cells. Phosphorylates PLCG1. Promotes phosphorylation of FYN, NCK1, NOS3, PIK3R1, PTK2/FAK1 and SRC.
N-glycosylated.
Ubiquitinated. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the receptor promotes its poly-ubiquitination, leading to its degradation via the proteasome or lysosomal proteases.
Autophosphorylated on tyrosine residues upon ligand binding. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans, i.e. one subunit of the dimeric receptor phosphorylates tyrosine residues on the other subunit. Phosphorylation at Tyr-951 is important for interaction with SH2D2A/TSAD and VEGFA-mediated reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Phosphorylation at Tyr-1175 is important for interaction with PLCG1 and SHB. Phosphorylation at Tyr-1214 is important for interaction with NCK1 and FYN. Dephosphorylated by PTPRB. Dephosphorylated by PTPRJ at Tyr-951, Tyr-996, Tyr-1054, Tyr-1059, Tyr-1175 and Tyr-1214.
The inhibitory disulfide bond between Cys-1024 and Cys-1045 may serve as a specific molecular switch for H(2)S-induced modification that regulates KDR/VEGFR2 function.
Cell junction. Endoplasmic reticulum.
Note: Localized with RAP1A at cell-cell junctions (By similarity). Colocalizes with ERN1 and XBP1 in the endoplasmic reticulum in endothelial cells in a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent manner (PubMed:23529610).
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Early endosome.
Note: Detected on caveolae-enriched lipid rafts at the cell surface. Is recycled from the plasma membrane to endosomes and back again. Phosphorylation triggered by VEGFA binding promotes internalization and subsequent degradation. VEGFA binding triggers internalization and translocation to the nucleus.
Secreted.
Secreted.
Detected in cornea (at protein level). Widely expressed.
Homodimer in the presence of bound dimeric VEGFA, VEGFC or VEGFD ligands; monomeric in the absence of bound ligands. Can also form heterodimers with FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2. Interacts (tyrosine phosphorylated) with LFYN, NCK1, PLCG1. Interacts (tyrosine-phosphorylated active form preferentially) with DAB2IP (via C2 domain and active form preferentially); the interaction occurs at the late phase of VEGFA response and inhibits KDR/VEGFR2 activity. Interacts with SHBSH2D2A/TSAD, GRB2, MYOF, CBL and PDCD6. Interacts (via C-terminus domain) with ERN1 (via kinase domain); the interaction is facilitated in a XBP1 isoform 1- and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent manner in endothelial cells. Interacts (via juxtamembrane region) with chaperone PDCL3 (via thioredoxin fold region); the interaction leads to increased KDR/VEGFR2 abundance through inhibition of its ubiquitination and degradation. Interacts (tyrosine phosphorylated) with CCDC88A/GIV (via SH2-like region); binding requires autophosphorylation of the KDR/VEGFR2 C-terminal region.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 Tat.
The second and third Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains are sufficient for VEGFC binding.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
文献引用
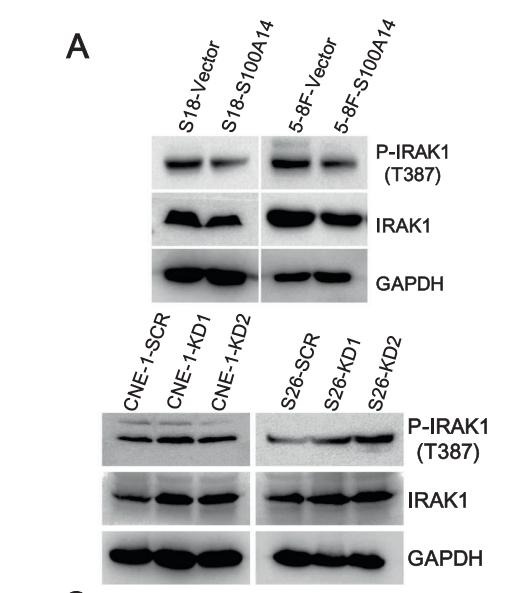
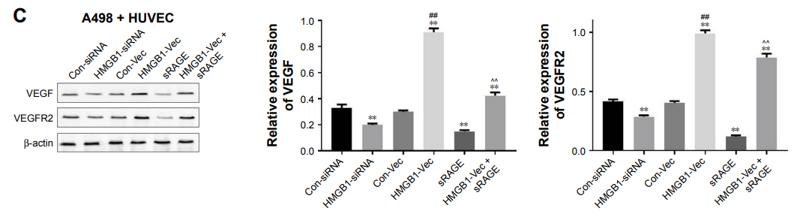
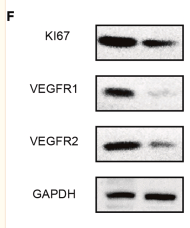
Application: WB Species: human Sample: PLC-PRF-5 cells
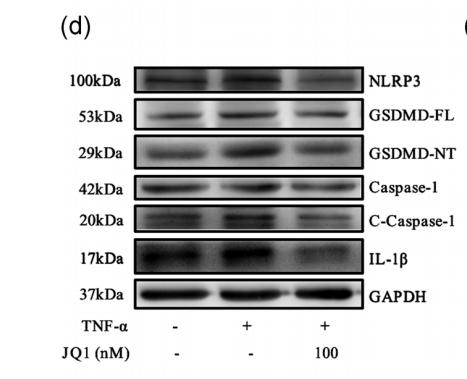
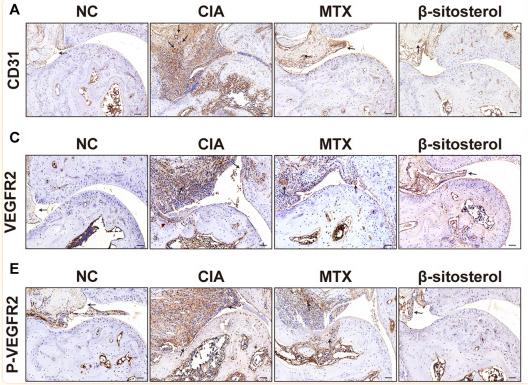
Application: IHC Species: human Sample: HCC
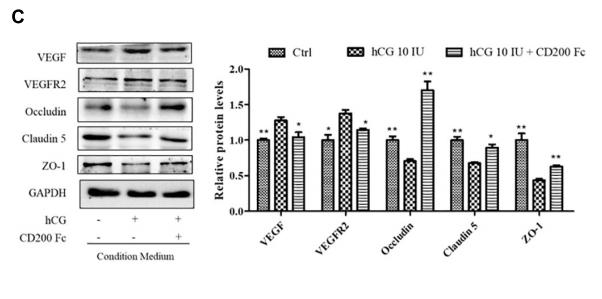
Application: IHC Species: Human Sample: ovarian tissue
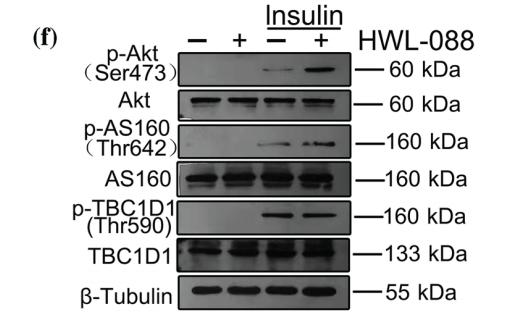
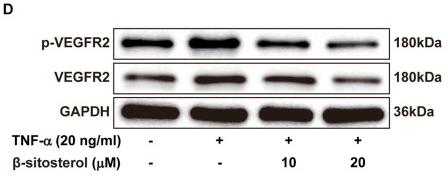
Application: WB Species: human Sample: PLC-PRF-5 cells
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.