| 产品: | YAP 抗体 |
| 货号: | AF6328 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to YAP |
| 应用: | WB IF/ICC |
| 文献验证: | WB, IF/ICC |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| 预测: | Pig, Zebrafish, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Chicken, Xenopus |
| 分子量: | 65~78kD; 54kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | P46937 |
| RRID: | AB_2835184 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6328, RRID:AB_2835184.
展开/折叠
65 kDa Yes associated protein; 65 kDa Yes-associated protein; COB1; YAp 1; YAP 65; YAP; YAP1; YAP1_HUMAN; YAP2; YAP65; yes -associated protein delta; Yes associated protein 1 65kDa; Yes associated protein 1; Yes associated protein 2; yes associated protein beta; YKI; Yorkie homolog;
抗原和靶标
Increased expression seen in some liver and prostate cancers. Isoforms lacking the transactivation domain found in striatal neurons of patients with Huntington disease (at protein level).
- P46937 YAP1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDPGQQPPPQPAPQGQGQPPSQPPQGQGPPSGPGQPAPAATQAAPQAPPAGHQIVHVRGDSETDLEALFNAVMNPKTANVPQTVPMRLRKLPDSFFKPPEPKSHSRQASTDAGTAGALTPQHVRAHSSPASLQLGAVSPGTLTPTGVVSGPAATPTAQHLRQSSFEIPDDVPLPAGWEMAKTSSGQRYFLNHIDQTTTWQDPRKAMLSQMNVTAPTSPPVQQNMMNSASGPLPDGWEQAMTQDGEIYYINHKNKTTSWLDPRLDPRFAMNQRISQSAPVKQPPPLAPQSPQGGVMGGSNSNQQQQMRLQQLQMEKERLRLKQQELLRQAMRNINPSTANSPKCQELALRSQLPTLEQDGGTQNPVSSPGMSQELRTMTTNSSDPFLNSGTYHSRDESTDSGLSMSSYSVPRTPDDFLNSVDEMDTGDTINQSTLPSQQNRFPDYLEAIPGTNVDLGTLEGDGMNIEGEELMPSLQEALSSDILNDMESVLAATKLDKESFLTWL
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Transcriptional regulator which can act both as a coactivator and a corepressor and is the critical downstream regulatory target in the Hippo signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. Plays a key role in tissue tension and 3D tissue shape by regulating cortical actomyosin network formation. Acts via ARHGAP18, a Rho GTPase activating protein that suppresses F-actin polymerization. Plays a key role to control cell proliferation in response to cell contact. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS1/2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration. The presence of TEAD transcription factors are required for it to stimulate gene expression, cell growth, anchorage-independent growth, and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) induction.
Isoform 2 and isoform 3 can activate the C-terminal fragment (CTF) of ERBB4 (isoform 3).
Phosphorylated by LATS1 and LATS2; leading to cytoplasmic translocation and inactivation. Phosphorylated by ABL1; leading to YAP1 stabilization, enhanced interaction with TP73 and recruitment onto proapoptotic genes; in response to DNA damage. Phosphorylation at Ser-400 and Ser-403 by CK1 is triggered by previous phosphorylation at Ser-397 by LATS proteins and leads to YAP1 ubiquitination by SCF(beta-TRCP) E3 ubiquitin ligase and subsequent degradation. Phosphorylated at Thr-119, Ser-138, Thr-154, Ser-367 and Thr-412 by MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK9/JNK2, which is required for the regulation of apoptosis by YAP1.
Ubiquitinated by SCF(beta-TRCP) E3 ubiquitin ligase.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Both phosphorylation and cell density can regulate its subcellular localization. Phosphorylation sequesters it in the cytoplasm by inhibiting its translocation into the nucleus. At low density, predominantly nuclear and is translocated to the cytoplasm at high density (PubMed:18158288, PubMed:20048001). PTPN14 induces translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (PubMed:22525271).
Increased expression seen in some liver and prostate cancers. Isoforms lacking the transactivation domain found in striatal neurons of patients with Huntington disease (at protein level).
Binds to the SH3 domain of the YES kinase. Binds to WBP1 and WBP2. Binds, in vitro, through the WW1 domain, to neural isoforms of ENAH that contain the PPSY motif (By similarity). The phosphorylated form interacts with YWHAB. Interacts (via WW domains) with LATS1 (via PPxY motif 2). Interacts with LATS2. Isoform 2 and isoform 3 interact (via WW domain 1) with isoform 3 of ERBB4 (via PPxY motif 2). Interacts with TEAD1, TEAD2, TEAD3 and TEAD4. Interacts with TP73. Interacts with RUNX1. Interacts with HCK. Interacts (via WW domains) with PTPN14 (via PPxY motif 2); this interaction leads to the cytoplasmic sequestration of YAP1 and inhibits its transcriptional coactivator activity.
The first coiled-coil region mediates most of the interaction with TEAD transcription factors.
Belongs to the YAP1 family.
研究领域
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
文献引用
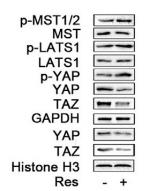
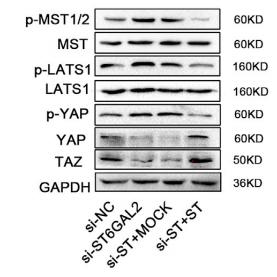
Application: WB Species: human Sample: FTC238 cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: FTC cells
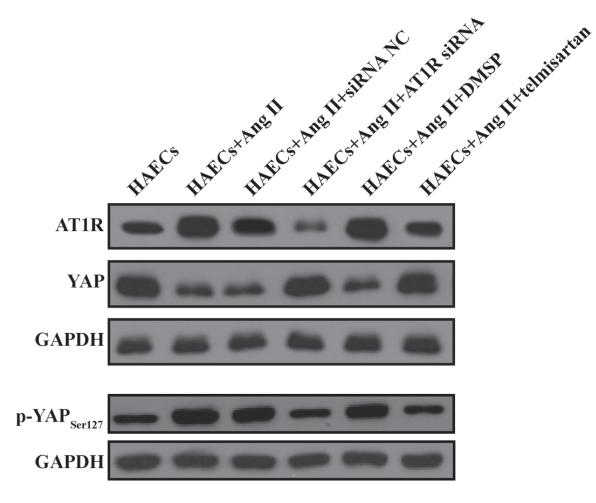
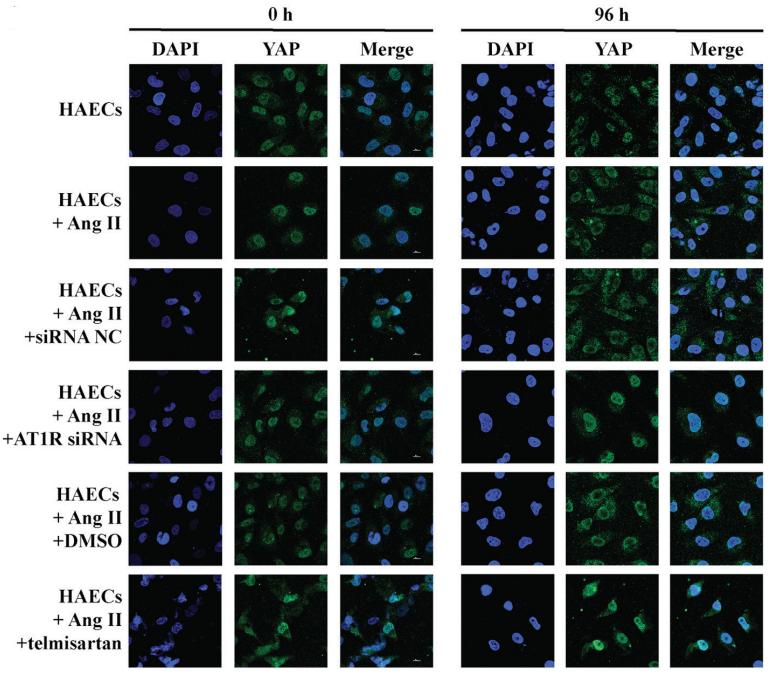
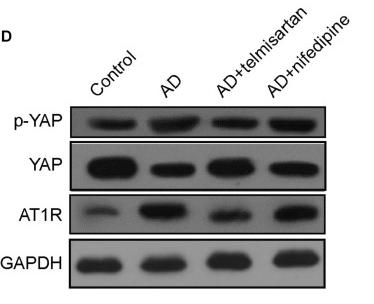
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: aortic tissue
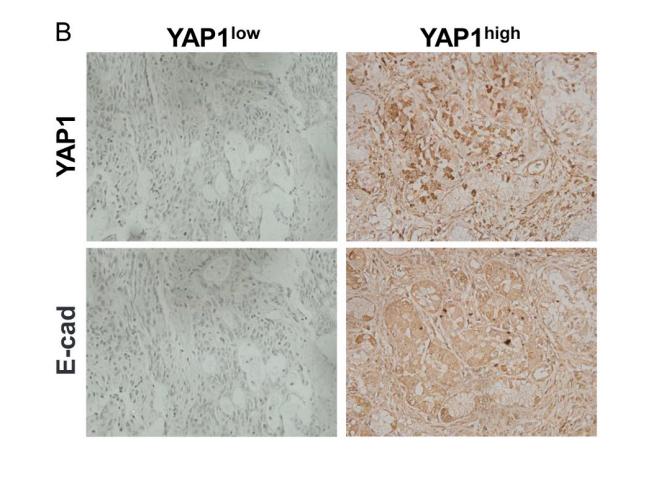
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: CCAs
Application: IHC Species: Mice Sample: tumor tissues
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.