产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF5045, RRID:AB_2837404.
展开/折叠
hMOP; LMOR; M-OR-1; MOP; MOR; MOR-1; MOR1; Mu opiate receptor; Mu opioid receptor; Mu-type opioid receptor; Opioid receptor mu 1; OPRM; OPRM_HUMAN; OPRM1;
抗原和靶标
- P35372 OPRM_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDSSAAPTNASNCTDALAYSSCSPAPSPGSWVNLSHLDGNLSDPCGPNRTDLGGRDSLCPPTGSPSMITAITIMALYSIVCVVGLFGNFLVMYVIVRYTKMKTATNIYIFNLALADALATSTLPFQSVNYLMGTWPFGTILCKIVISIDYYNMFTSIFTLCTMSVDRYIAVCHPVKALDFRTPRNAKIINVCNWILSSAIGLPVMFMATTKYRQGSIDCTLTFSHPTWYWENLLKICVFIFAFIMPVLIITVCYGLMILRLKSVRMLSGSKEKDRNLRRITRMVLVVVAVFIVCWTPIHIYVIIKALVTIPETTFQTVSWHFCIALGYTNSCLNPVLYAFLDENFKRCFREFCIPTSSNIEQQNSTRIRQNTRDHPSTANTVDRTNHQLENLEAETAPLP
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Receptor for endogenous opioids such as beta-endorphin and endomorphin. Receptor for natural and synthetic opioids including morphine, heroin, DAMGO, fentanyl, etorphine, buprenorphin and methadone. Agonist binding to the receptor induces coupling to an inactive GDP-bound heterotrimeric G-protein complex and subsequent exchange of GDP for GTP in the G-protein alpha subunit leading to dissociation of the G-protein complex with the free GTP-bound G-protein alpha and the G-protein beta-gamma dimer activating downstream cellular effectors. The agonist- and cell type-specific activity is predominantly coupled to pertussis toxin-sensitive G(i) and G(o) G alpha proteins, GNAI1, GNAI2, GNAI3 and GNAO1 isoforms Alpha-1 and Alpha-2, and to a lesser extent to pertussis toxin-insensitive G alpha proteins GNAZ and GNA15. They mediate an array of downstream cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity and both N-type and L-type calcium channels, activation of inward rectifying potassium channels, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phospholipase C (PLC), phosphoinositide/protein kinase (PKC), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and regulation of NF-kappa-B. Also couples to adenylate cyclase stimulatory G alpha proteins. The selective temporal coupling to G-proteins and subsequent signaling can be regulated by RGSZ proteins, such as RGS9, RGS17 and RGS4. Phosphorylation by members of the GPRK subfamily of Ser/Thr protein kinases and association with beta-arrestins is involved in short-term receptor desensitization. Beta-arrestins associate with the GPRK-phosphorylated receptor and uncouple it from the G-protein thus terminating signal transduction. The phosphorylated receptor is internalized through endocytosis via clathrin-coated pits which involves beta-arrestins. The activation of the ERK pathway occurs either in a G-protein-dependent or a beta-arrestin-dependent manner and is regulated by agonist-specific receptor phosphorylation. Acts as a class A G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) which dissociates from beta-arrestin at or near the plasma membrane and undergoes rapid recycling. Receptor down-regulation pathways are varying with the agonist and occur dependent or independent of G-protein coupling. Endogenous ligands induce rapid desensitization, endocytosis and recycling whereas morphine induces only low desensitization and endocytosis. Heterooligomerization with other GPCRs can modulate agonist binding, signaling and trafficking properties. Involved in neurogenesis. Isoform 12 couples to GNAS and is proposed to be involved in excitatory effects. Isoform 16 and isoform 17 do not bind agonists but may act through oligomerization with binding-competent OPRM1 isoforms and reduce their ligand binding activity.
Phosphorylated. Differentially phosphorylated in basal and agonist-induced conditions. Agonist-mediated phosphorylation modulates receptor internalization. Phosphorylated by GRK2 in a agonist-dependent manner. Phosphorylation at Tyr-168 requires receptor activation, is dependent on non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase Src and results in a decrease in agonist efficacy by reducing G-protein coupling efficiency. Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues; the phosphorylation is involved in agonist-induced G-protein-independent receptor down-regulation. Phosphorylation at Ser-377 is involved in G-protein-dependent but not beta-arrestin-dependent activation of the ERK pathway (By similarity).
Ubiquitinated. A basal ubiquitination seems not to be related to degradation. Ubiquitination is increased upon formation of OPRM1:OPRD1 oligomers leading to proteasomal degradation; the ubiquitination is diminished by RTP4.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection>Axon. Perikaryon. Cell projection>Dendrite. Endosome.
Note: Is rapidly internalized after agonist binding.
Cytoplasm.
Expressed in brain. Isoform 16 and isoform 17 are detected in brain.
Forms homooligomers and heterooligomers with other GPCRs, such as OPRD1, OPRK1, OPRL1, NPFFR2, ADRA2A, SSTR2, CNR1 and CCR5 (probably in dimeric forms). Interacts with heterotrimeric G proteins; interaction with a heterotrimeric complex containing GNAI1, GNB1 and GNG2 stabilizes the active conformation of the receptor and increases its affinity for endomorphin-2, the synthetic opioid peptide DAMGO and for morphinan agonists (By similarity). Interacts with PPL; the interaction disrupts agonist-mediated G-protein activation. Interacts (via C-terminus) with DNAJB4 (via C-terminus). Interacts with calmodulin; the interaction inhibits the constitutive activity of OPRM1; it abolishes basal and attenuates agonist-stimulated G-protein coupling. Interacts with FLNA, PLD2, RANBP9 and WLS and GPM6A. Interacts with RTP4 (By similarity). Interacts with SYP and GNAS (By similarity). Interacts with RGS9, RGS17, RGS20, RGS4, PPP1R9B and HINT1 (By similarity).
Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family.
研究领域
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Morphine addiction.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
文献引用
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample:
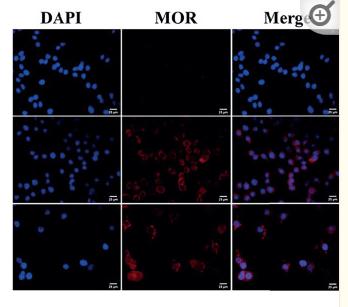
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mice Sample:
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: HCC tissues
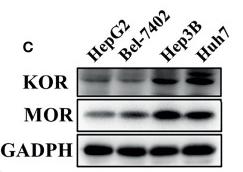
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HCC tissues
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.