| 产品: | XBP1 抗体 |
| 货号: | AF5110 |
| 描述: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to XBP1 |
| 应用: | WB IHC |
| 文献验证: | WB |
| 反应: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 预测: | Sheep, Dog |
| 分子量: | 30~45kD(Unspliced),55kD(Spliced).; 29kD(Calculated). |
| 蛋白号: | P17861 |
| RRID: | AB_2837596 |
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5110, RRID:AB_2837596.
展开/折叠
Tax responsive element binding protein 5; Tax-responsive element-binding protein 5; TREB5; X box binding protein 1; X box binding protein 2; X-box-binding protein 1; XBP 1; XBP-1; XBP1; XBP1_HUMAN; XBP2;
抗原和靶标
A synthesized peptide derived from human XBP1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Expressed in plasma cells in rheumatoid synovium (PubMed:11460154). Over-expressed in primary breast cancer and metastatic breast cancer cells (PubMed:25280941). Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are expressed at higher level in proliferating as compared to confluent quiescent endothelial cells (PubMed:19416856).
- P17861 XBP1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MVVVAAAPNPADGTPKVLLLSGQPASAAGAPAGQALPLMVPAQRGASPEAASGGLPQARKRQRLTHLSPEEKALRRKLKNRVAAQTARDRKKARMSELEQQVVDLEEENQKLLLENQLLREKTHGLVVENQELRQRLGMDALVAEEEAEAKGNEVRPVAGSAESAALRLRAPLQQVQAQLSPLQNISPWILAVLTLQIQSLISCWAFWTTWTQSCSSNALPQSLPAWRSSQRSTQKDPVPYQPPFLCQWGRHQPSWKPLMN
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Functions as a transcription factor during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by regulating the unfolded protein response (UPR). Required for cardiac myogenesis and hepatogenesis during embryonic development, and the development of secretory tissues such as exocrine pancreas and salivary gland (By similarity). Involved in terminal differentiation of B lymphocytes to plasma cells and production of immunoglobulins. Modulates the cellular response to ER stress in a PIK3R-dependent manner. Binds to the cis-acting X box present in the promoter regions of major histocompatibility complex class II genes. Involved in VEGF-induced endothelial cell (EC) proliferation and retinal blood vessel formation during embryonic development but also for angiogenesis in adult tissues under ischemic conditions. Functions also as a major regulator of the UPR in obesity-induced insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes for the management of obesity and diabetes prevention (By similarity).
Plays a role in the unconventional cytoplasmic splicing processing of its own mRNA triggered by the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transmembrane endoribonuclease ENR1: upon ER stress, the emerging XBP1 polypeptide chain, as part of a mRNA-ribosome-nascent chain (R-RNC) complex, cotranslationally recruits its own unprocessed mRNA through transient docking to the ER membrane and translational pausing, therefore facilitating efficient IRE1-mediated XBP1 mRNA isoform 2 production. In endothelial cells (EC), associated with KDR, promotes IRE1-mediated XBP1 mRNA isoform 2 productions in a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent manner, leading to EC proliferation and angiogenesis. Functions as a negative feed-back regulator of the potent transcription factor XBP1 isoform 2 protein levels through proteasome-mediated degradation, thus preventing the constitutive activation of the ER stress response signaling pathway. Inhibits the transactivation activity of XBP1 isoform 2 in myeloma cells (By similarity). Acts as a weak transcriptional factor. Together with HDAC3, contributes to the activation of NFE2L2-mediated HMOX1 transcription factor gene expression in a PI(3)K/mTORC2/Akt-dependent signaling pathway leading to EC survival under disturbed flow/oxidative stress. Binds to the ER stress response element (ERSE) upon ER stress. Binds to the consensus 5'-GATGACGTG[TG]N(3)[AT]T-3' sequence related to cAMP responsive element (CRE)-like sequences. Binds the Tax-responsive element (TRE) present in the long terminal repeat (LTR) of T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-I) and to the TPA response elements (TRE). Associates preferentially to the HDAC3 gene promoter region in a static flow-dependent manner. Binds to the CDH5/VE-cadherin gene promoter region.
Functions as a stress-inducible potent transcriptional activator during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by inducing unfolded protein response (UPR) target genes via binding to the UPR element (UPRE). Up-regulates target genes encoding ER chaperones and ER-associated degradation (ERAD) components to enhance the capacity of productive folding and degradation mechanism, respectively, in order to maintain the homeostasis of the ER under ER stress. Plays a role in the production of immunoglobulins and interleukin-6 in the presence of stimuli required for plasma cell differentiation (By similarity). Induces phospholipid biosynthesis and ER expansion. Contributes to the VEGF-induced endothelial cell (EC) growth and proliferation in a Akt/GSK-dependent and/or -independent signaling pathway, respectively, leading to beta-catenin nuclear translocation and E2F2 gene expression. Promotes umbilical vein EC apoptosis and atherosclerotisis development in a caspase-dependent signaling pathway, and contributes to VEGF-induced EC proliferation and angiogenesis in adult tissues under ischemic conditions. Involved in the regulation of endostatin-induced autophagy in EC through BECN1 transcriptional activation. Plays a role as an oncogene by promoting tumor progression: stimulates zinc finger protein SNAI1 transcription to induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal (EMT) transition, cell migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Involved in adipocyte differentiation by regulating lipogenic gene expression during lactation. Plays a role in the survival of both dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc), by maintaining protein homeostasis and of myeloma cells. Increases insulin sensitivity in the liver as a response to a high carbohydrate diet, resulting in improved glucose tolerance. Improves also glucose homeostasis in an ER stress- and/or insulin-independent manner through both binding and proteasome-induced degradation of the transcription factor FOXO1, hence resulting in suppression of gluconeogenic genes expression and in a reduction of blood glucose levels. Controls the induction of de novo fatty acid synthesis in hepatocytes by regulating the expression of a subset of lipogenic genes in an ER stress- and UPR-independent manner (By similarity). Associates preferentially to the HDAC3 gene promoter region in a disturbed flow-dependent manner. Binds to the BECN1 gene promoter region. Binds to the CDH5/VE-cadherin gene promoter region. Binds to the ER stress response element (ERSE) upon ER stress. Binds to the 5'-CCACG-3' motif in the PPARG promoter (By similarity).
Isoform 2 is acetylated by EP300; acetylation positively regulates the transcriptional activity of XBP1 isoform 2. Isoform 2 is deacetylated by SIRT1; deacetylation negatively regulates the transcriptional activity of XBP1 isoform 2.
Isoform 1 is ubiquitinated, leading to proteasome-mediated degradation in response to ER stress.
X-box-binding protein 1, cytoplasmic form and luminal form are produced by intramembrane proteolytic cleavage of ER membrane-anchored isoform 1 triggered by HM13/SPP in a DERL1-RNF139-dependent and VCP/p97-independent manner. X-box-binding protein 1, luminal form is ubiquitinated leading to proteasomal degradation.
Endoplasmic reticulum.
Note: Colocalizes with ERN1 and KDR in the endoplasmic reticulum in endothelial cells in a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent manner (PubMed:23529610).
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane>Single-pass type II membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Membrane>Peripheral membrane protein.
Note: Shows no preferential localization to either the nucleus or the cytoplasm (By similarity). Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in a CRM1-dependent manner (PubMed:16461360). Localizes predominantly at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane as a membrane-spanning protein; whereas may be only marginally localized on the cytosolic side of the ER membrane as a peripheral membrane (PubMed:19394296, PubMed:25190803).
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Note: Localizes predominantly in the nucleus. Colocalizes in the nucleus with SIRT1. Translocates into the nucleus in a PIK3R-, ER stress-induced- and/or insulin-dependent manner (By similarity).
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Localizes in the cytoplasm and nucleus after HM13/SPP-mediated intramembranaire proteolytic cleavage of isoform 1 (PubMed:25239945).
Expressed in plasma cells in rheumatoid synovium. Over-expressed in primary breast cancer and metastatic breast cancer cells. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are expressed at higher level in proliferating as compared to confluent quiescent endothelial cells.
Isoform 2 interacts with SIRT1. Isoform 2 interacts with PIK3R1 and PIK3R2; the interactions are direct and induce translocation of XBP1 isoform 2 into the nucleus and the unfolded protein response (UPR) XBP1-dependent target genes activation in a ER stress- and/or insulin-dependent but PI3K-independent manner. Isoform 2 interacts with FOXO1; the interaction is direct and leads to FOXO1 ubiquitination and degradation via the proteasome pathway in hepatocytes (By similarity). Isoform 1 interacts with HM13. Isoform 1 interacts with RNF139; the interaction induces ubiquitination and degradation of isoform 1. Isoform 1 interacts (via luminal domain) with DERL1; the interaction obviates the need for ectodomain shedding prior HM13/SPP-mediated XBP1 isoform 1 cleavage. Isoform 1 interacts with isoform 2; the interaction sequesters isoform 2 from the nucleus and enhances isoform 2 degradation in the cytoplasm. Isoform 1 interacts with HDAC3 and AKT1; the interactions occur in endothelial cell (EC) under disturbed flow. Isoform 1 interacts with the oncoprotein FOS. Isoform 2 interacts with ATF6; the interaction occurs in a ER stress-dependent manner and is required for DNA binding to the unfolded protein response element (UPRE). Isoform 2 interacts with PIK3R1; the interaction is direct and induces translocation of XBP1 isoform 2 into the nucleus and the unfolded protein response (UPR) XBP1-dependent target genes activation in a ER stress- and/or insulin-dependent but PI3K-independent manner.
Isoform 1 and isoform 2 N-terminus domains are necessary for nuclear localization targeting. Isoform 1 C-terminus domain confers localization to the cytoplasm and is sufficient to impose rapid degradation (By similarity). Isoform 1 transmembrane signal-anchor domain is necessary for its own mRNA to be recruited to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) which will undergo unconventional ERN1-dependent splicing in response to ER stress (PubMed:19394296, PubMed:21233347). Isoform 1 N-terminus and C-terminus regions are necessary for DNA-binding and weak transcriptional activity, respectively. Isoform 2 N-terminus and C-terminus regions are necessary for DNA-binding and strong transcriptional activity upon ER stress, respectively (PubMed:11779464, PubMed:8657566). Isoform 2 C-terminus region contains a nuclear exclusion signal (NES) at positions 186 through 208. Isoform 2 C-terminus region contains a degradation domain at positions 209 through 261 (PubMed:16461360).
Belongs to the bZIP family.
研究领域
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
文献引用
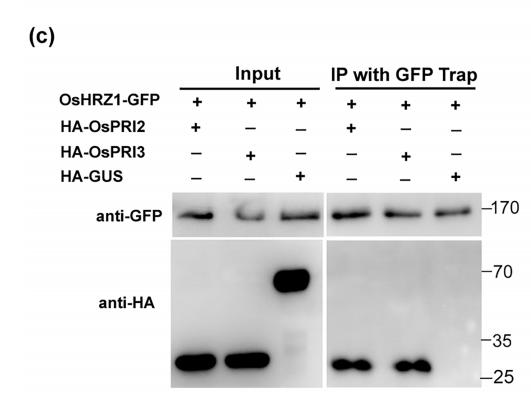
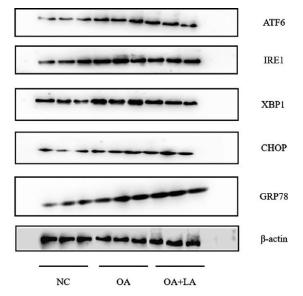
Application: WB Species: human Sample: Molm13 cell
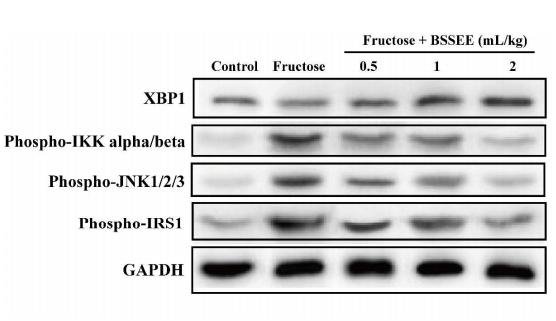
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: Liver
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: HSC-T6 cells
Application: WB Species: rat Sample:
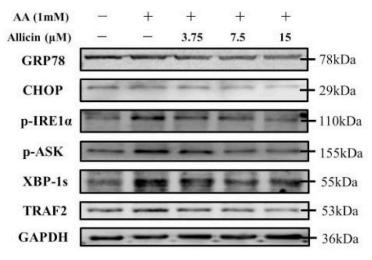
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HepG2 cells
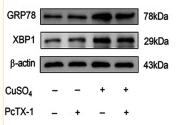
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.