产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5139, RRID:AB_2837625.
展开/折叠
Tetraspanin 29; 5H9; 5H9 antigen; Antigen defined by monoclonal antibody 602 29; Antigen defined by monoclonal antibody 60229; BA-2/p24 antigen; BA2; BTCC 1; BTCC1; CD9; CD9 antigen; CD9 antigen p24; CD9 molecule; CD9_HUMAN; Cell growth inhibiting gene 2 protein; Cell growth-inhibiting gene 2 protein; DRAP 27; DRAP27; GIG2; Growth inhibiting gene 2 protein; Leukocyte antigen MIC3; MIC3; Motility related protein; Motility-related protein; MRP 1; MRP-1; MRP1; p24; p24 antigen; Tetraspanin-29; Tspan 29; Tspan-29; TSPAN29;
抗原和靶标
A synthesized peptide derived from human CD9, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Detected in platelets (at protein level) (PubMed:19640571). Expressed by a variety of hematopoietic and epithelial cells (PubMed:19640571).
- P21926 CD9_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPVKGGTKCIKYLLFGFNFIFWLAGIAVLAIGLWLRFDSQTKSIFEQETNNNNSSFYTGVYILIGAGALMMLVGFLGCCGAVQESQCMLGLFFGFLLVIFAIEIAAAIWGYSHKDEVIKEVQEFYKDTYNKLKTKDEPQRETLKAIHYALNCCGLAGGVEQFISDICPKKDVLETFTVKSCPDAIKEVFDNKFHIIGAVGIGIAVVMIFGMIFSMILCCAIRRNREMV
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Integral membrane protein associated with integrins, which regulates different processes, such as sperm-egg fusion, platelet activation and aggregation, and cell adhesion. Present at the cell surface of oocytes and plays a key role in sperm-egg fusion, possibly by organizing multiprotein complexes and the morphology of the membrane required for the fusion (By similarity). In myoblasts, associates with CD81 and PTGFRN and inhibits myotube fusion during muscle regeneration (By similarity). In macrophages, associates with CD81 and beta-1 and beta-2 integrins, and prevents macrophage fusion into multinucleated giant cells specialized in ingesting complement-opsonized large particles. Also prevents the fusion between mononuclear cell progenitors into osteoclasts in charge of bone resorption (By similarity). Acts as a receptor for PSG17 (By similarity). Involved in platelet activation and aggregation. Regulates paranodal junction formation (By similarity). Involved in cell adhesion, cell motility and tumor metastasis.
Palmitoylated at a low, basal level in unstimulated platelets. The level of palmitoylation increases when platelets are activated by thrombin (in vitro). The protein exists in three forms with molecular masses between 22 and 27 kDa, and is known to carry covalently linked fatty acids.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Secreted>Extracellular exosome.
Note: Present at the cell surface of oocytes. Accumulates in the adhesion area between the sperm and egg following interaction between IZUMO1 and its receptor IZUMO1R/JUNO.
Detected in platelets (at protein level). Expressed by a variety of hematopoietic and epithelial cells.
Belongs to the tetraspanin (TM4SF) family.
研究领域
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Hematopoietic cell lineage. (View pathway)
文献引用
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
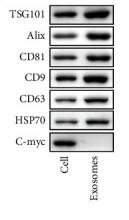
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HEK293T cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HEK293T cells
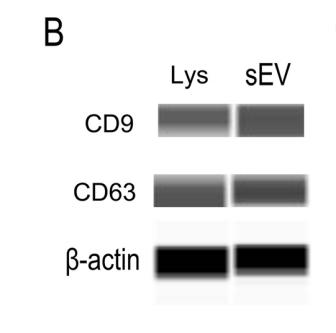
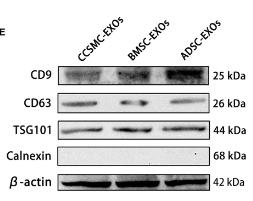
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: DPSCs-sEV
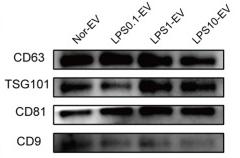
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
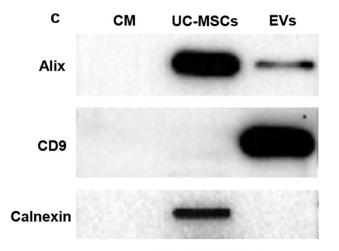
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: SCAPs
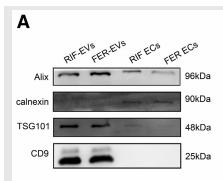
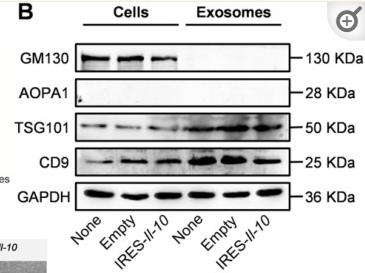
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: RIF-EVs and FER-EVs.
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.