产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5178, RRID:AB_2837664.
展开/折叠
AD2; Apo-E; APOE; APOE_HUMAN; APOEA; Apolipoprotein E; Apolipoprotein E3; ApolipoproteinE; Apoprotein; LDLCQ5; LPG;
抗原和靶标
Produced by several tissues and cell types and mainly found associated with lipid particles in the plasma, the interstitial fluid and lymph (PubMed:25173806). Mainly synthesized by liver hepatocytes (PubMed:25173806). Significant quantities are also produced in brain, mainly by astrocytes and glial cells in the cerebral cortex, but also by neurons in frontal cortex and hippocampus (PubMed:3115992, PubMed:10027417). It is also expressed by cells of the peripheral nervous system (PubMed:10027417, PubMed:25173806). Also expressed by adrenal gland, testis, ovary, skin, kidney, spleen and adipose tissue and macrophages in various tissues (PubMed:25173806).
- P02649 APOE_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MKVLWAALLVTFLAGCQAKVEQAVETEPEPELRQQTEWQSGQRWELALGRFWDYLRWVQTLSEQVQEELLSSQVTQELRALMDETMKELKAYKSELEEQLTPVAEETRARLSKELQAAQARLGADMEDVCGRLVQYRGEVQAMLGQSTEELRVRLASHLRKLRKRLLRDADDLQKRLAVYQAGAREGAERGLSAIRERLGPLVEQGRVRAATVGSLAGQPLQERAQAWGERLRARMEEMGSRTRDRLDEVKEQVAEVRAKLEEQAQQIRLQAEAFQARLKSWFEPLVEDMQRQWAGLVEKVQAAVGTSAAPVPSDNH
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
APOE is an apolipoprotein, a protein associating with lipid particles, that mainly functions in lipoprotein-mediated lipid transport between organs via the plasma and interstitial fluids. APOE is a core component of plasma lipoproteins and is involved in their production, conversion and clearance. Apoliproteins are amphipathic molecules that interact both with lipids of the lipoprotein particle core and the aqueous environment of the plasma. As such, APOE associates with chylomicrons, chylomicron remnants, very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL) but shows a preferential binding to high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It also binds a wide range of cellular receptors including the LDL receptor/LDLR, the LDL receptor-related proteins LRP1, LRP2 and LRP8 and the very low-density lipoprotein receptor/VLDLR that mediate the cellular uptake of the APOE-containing lipoprotein particles. Finally, APOE has also a heparin-binding activity and binds heparan-sulfate proteoglycans on the surface of cells, a property that supports the capture and the receptor-mediated uptake of APOE-containing lipoproteins by cells. A main function of APOE is to mediate lipoprotein clearance through the uptake of chylomicrons, VLDLs, and HDLs by hepatocytes. APOE is also involved in the biosynthesis by the liver of VLDLs as well as their uptake by peripheral tissues ensuring the delivery of triglycerides and energy storage in muscle, heart and adipose tissues. By participating to the lipoprotein-mediated distribution of lipids among tissues, APOE plays a critical role in plasma and tissues lipid homeostasis. APOE is also involved in two steps of reverse cholesterol transport, the HDLs-mediated transport of cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver, and thereby plays an important role in cholesterol homeostasis. First, it is functionally associated with ABCA1 in the biogenesis of HDLs in tissues. Second, it is enriched in circulating HDLs and mediates their uptake by hepatocytes. APOE also plays an important role in lipid transport in the central nervous system, regulating neuron survival and sprouting. APOE in also involved in innate and adaptive immune responses, controlling for instance the survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (By similarity). APOE, may also play a role in transcription regulation through a receptor-dependent and cholesterol-independent mechanism, that activates MAP3K12 and a non-canonical MAPK signal transduction pathway that results in enhanced AP-1-mediated transcription of APP.
APOE exists as multiple glycosylated and sialylated glycoforms within cells and in plasma. The extent of glycosylation and sialylation are tissue and context specific. Plasma APOE undergoes desialylation and is less glycosylated and sialylated than the cellular form. Glycosylation is not required for proper expression and secretion. O-glycosylated with core 1 or possibly core 8 glycans. Thr-307 and Ser-314 are minor glycosylation sites compared to Ser-308.
Glycated in plasma VLDL of normal subjects, and of hyperglycemic diabetic patients at a higher level (2-3 fold).
Phosphorylated by FAM20C in the extracellular medium.
Undergoes C-terminal proteolytic processing in neurons. C-terminally truncated APOE has a tendency to form neurotoxic intracellular neurofibrillary tangle-like inclusions in neurons.
Secreted. Secreted>Extracellular space. Secreted>Extracellular space>Extracellular matrix.
Note: In the plasma, APOE is associated with chylomicrons, chylomicrons remnants, VLDL, LDL and HDL lipoproteins (PubMed:1911868, PubMed:8340399). Lipid poor oligomeric APOE is associated with the extracellular matrix in a calcium- and heparan-sulfate proteoglycans-dependent manner (PubMed:9488694). Lipidation induces the release from the extracellular matrix (PubMed:9488694).
Produced by several tissues and cell types and mainly found associated with lipid particles in the plasma, the interstitial fluid and lymph. Mainly synthesized by liver hepatocytes. Significant quantities are also produced in brain, mainly by astrocytes and glial cells in the cerebral cortex, but also by neurons in frontal cortex and hippocampus. It is also expressed by cells of the peripheral nervous system. Also expressed by adrenal gland, testis, ovary, skin, kidney, spleen and adipose tissue and macrophages in various tissues.
Homotetramer. May interact with ABCA1; functionally associated with ABCA1 in the biogenesis of HDLs. May interact with APP/A4 amyloid-beta peptide; the interaction is extremely stable in vitro but its physiological significance is unclear. May interact with MAPT. May interact with MAP2. In the cerebrospinal fluid, interacts with secreted SORL1.
Belongs to the apolipoprotein A1/A4/E family.
研究领域
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Cholesterol metabolism.
文献引用
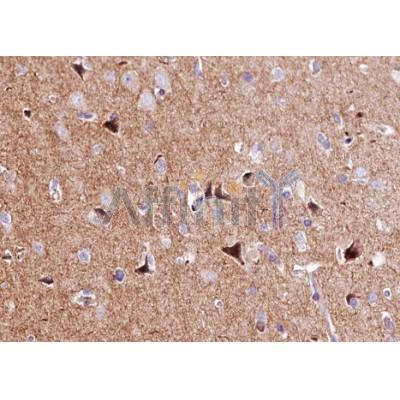
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: hippocampus
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.