产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5360, RRID:AB_2837845.
展开/折叠
E1A associated protein p300; E1A binding protein p300; E1A-associated protein p300; EP300; EP300: E1A binding protein p300; EP300_HUMAN; Histone acetyltransferase p300; KAT3B; p300 HAT; RSTS2;
抗原和靶标
- Q09472 EP300_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAENVVEPGPPSAKRPKLSSPALSASASDGTDFGSLFDLEHDLPDELINSTELGLTNGGDINQLQTSLGMVQDAASKHKQLSELLRSGSSPNLNMGVGGPGQVMASQAQQSSPGLGLINSMVKSPMTQAGLTSPNMGMGTSGPNQGPTQSTGMMNSPVNQPAMGMNTGMNAGMNPGMLAAGNGQGIMPNQVMNGSIGAGRGRQNMQYPNPGMGSAGNLLTEPLQQGSPQMGGQTGLRGPQPLKMGMMNNPNPYGSPYTQNPGQQIGASGLGLQIQTKTVLSNNLSPFAMDKKAVPGGGMPNMGQQPAPQVQQPGLVTPVAQGMGSGAHTADPEKRKLIQQQLVLLLHAHKCQRREQANGEVRQCNLPHCRTMKNVLNHMTHCQSGKSCQVAHCASSRQIISHWKNCTRHDCPVCLPLKNAGDKRNQQPILTGAPVGLGNPSSLGVGQQSAPNLSTVSQIDPSSIERAYAALGLPYQVNQMPTQPQVQAKNQQNQQPGQSPQGMRPMSNMSASPMGVNGGVGVQTPSLLSDSMLHSAINSQNPMMSENASVPSLGPMPTAAQPSTTGIRKQWHEDITQDLRNHLVHKLVQAIFPTPDPAALKDRRMENLVAYARKVEGDMYESANNRAEYYHLLAEKIYKIQKELEEKRRTRLQKQNMLPNAAGMVPVSMNPGPNMGQPQPGMTSNGPLPDPSMIRGSVPNQMMPRITPQSGLNQFGQMSMAQPPIVPRQTPPLQHHGQLAQPGALNPPMGYGPRMQQPSNQGQFLPQTQFPSQGMNVTNIPLAPSSGQAPVSQAQMSSSSCPVNSPIMPPGSQGSHIHCPQLPQPALHQNSPSPVPSRTPTPHHTPPSIGAQQPPATTIPAPVPTPPAMPPGPQSQALHPPPRQTPTPPTTQLPQQVQPSLPAAPSADQPQQQPRSQQSTAASVPTPTAPLLPPQPATPLSQPAVSIEGQVSNPPSTSSTEVNSQAIAEKQPSQEVKMEAKMEVDQPEPADTQPEDISESKVEDCKMESTETEERSTELKTEIKEEEDQPSTSATQSSPAPGQSKKKIFKPEELRQALMPTLEALYRQDPESLPFRQPVDPQLLGIPDYFDIVKSPMDLSTIKRKLDTGQYQEPWQYVDDIWLMFNNAWLYNRKTSRVYKYCSKLSEVFEQEIDPVMQSLGYCCGRKLEFSPQTLCCYGKQLCTIPRDATYYSYQNRYHFCEKCFNEIQGESVSLGDDPSQPQTTINKEQFSKRKNDTLDPELFVECTECGRKMHQICVLHHEIIWPAGFVCDGCLKKSARTRKENKFSAKRLPSTRLGTFLENRVNDFLRRQNHPESGEVTVRVVHASDKTVEVKPGMKARFVDSGEMAESFPYRTKALFAFEEIDGVDLCFFGMHVQEYGSDCPPPNQRRVYISYLDSVHFFRPKCLRTAVYHEILIGYLEYVKKLGYTTGHIWACPPSEGDDYIFHCHPPDQKIPKPKRLQEWYKKMLDKAVSERIVHDYKDIFKQATEDRLTSAKELPYFEGDFWPNVLEESIKELEQEEEERKREENTSNESTDVTKGDSKNAKKKNNKKTSKNKSSLSRGNKKKPGMPNVSNDLSQKLYATMEKHKEVFFVIRLIAGPAANSLPPIVDPDPLIPCDLMDGRDAFLTLARDKHLEFSSLRRAQWSTMCMLVELHTQSQDRFVYTCNECKHHVETRWHCTVCEDYDLCITCYNTKNHDHKMEKLGLGLDDESNNQQAAATQSPGDSRRLSIQRCIQSLVHACQCRNANCSLPSCQKMKRVVQHTKGCKRKTNGGCPICKQLIALCCYHAKHCQENKCPVPFCLNIKQKLRQQQLQHRLQQAQMLRRRMASMQRTGVVGQQQGLPSPTPATPTTPTGQQPTTPQTPQPTSQPQPTPPNSMPPYLPRTQAAGPVSQGKAAGQVTPPTPPQTAQPPLPGPPPAAVEMAMQIQRAAETQRQMAHVQIFQRPIQHQMPPMTPMAPMGMNPPPMTRGPSGHLEPGMGPTGMQQQPPWSQGGLPQPQQLQSGMPRPAMMSVAQHGQPLNMAPQPGLGQVGISPLKPGTVSQQALQNLLRTLRSPSSPLQQQQVLSILHANPQLLAAFIKQRAAKYANSNPQPIPGQPGMPQGQPGLQPPTMPGQQGVHSNPAMQNMNPMQAGVQRAGLPQQQPQQQLQPPMGGMSPQAQQMNMNHNTMPSQFRDILRRQQMMQQQQQQGAGPGIGPGMANHNQFQQPQGVGYPPQQQQRMQHHMQQMQQGNMGQIGQLPQALGAEAGASLQAYQQRLLQQQMGSPVQPNPMSPQQHMLPNQAQSPHLQGQQIPNSLSNQVRSPQPVPSPRPQSQPPHSSPSPRMQPQPSPHHVSPQTSSPHPGLVAAQANPMEQGHFASPDQNSMLSQLASNPGMANLHGASATDLGLSTDNSDLNSNLSQSTLDIH
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Functions as histone acetyltransferase and regulates transcription via chromatin remodeling. Acetylates all four core histones in nucleosomes. Histone acetylation gives an epigenetic tag for transcriptional activation. Mediates cAMP-gene regulation by binding specifically to phosphorylated CREB protein. Mediates acetylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-122' (H3K122ac), a modification that localizes at the surface of the histone octamer and stimulates transcription, possibly by promoting nucleosome instability. Mediates acetylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-27' (H3K27ac). Also functions as acetyltransferase for non-histone targets, such as ALX1, HDAC1, PRMT1 or SIRT2. Acetylates 'Lys-131' of ALX1 and acts as its coactivator. Acetylates SIRT2 and is proposed to indirectly increase the transcriptional activity of TP53 through acetylation and subsequent attenuation of SIRT2 deacetylase function. Acetylates HDAC1 leading to its inactivation and modulation of transcription. Acts as a TFAP2A-mediated transcriptional coactivator in presence of CITED2. Plays a role as a coactivator of NEUROD1-dependent transcription of the secretin and p21 genes and controls terminal differentiation of cells in the intestinal epithelium. Promotes cardiac myocyte enlargement. Can also mediate transcriptional repression. Acetylates FOXO1 and enhances its transcriptional activity. Acetylates BCL6 wich disrupts its ability to recruit histone deacetylases and hinders its transcriptional repressor activity. Participates in CLOCK or NPAS2-regulated rhythmic gene transcription; exhibits a circadian association with CLOCK or NPAS2, correlating with increase in PER1/2 mRNA and histone H3 acetylation on the PER1/2 promoter. Acetylates MTA1 at 'Lys-626' which is essential for its transcriptional coactivator activity. Acetylates XBP1 isoform 2; acetylation increases protein stability of XBP1 isoform 2 and enhances its transcriptional activity. Acetylates PCNA; acetylation promotes removal of chromatin-bound PCNA and its degradation during nucleotide excision repair (NER). Acetylates MEF2D. Acetylates and stabilizes ZBTB7B protein by antagonizing ubiquitin conjugation and degragation, this mechanism may be involved in CD4/CD8 lineage differentiation. Acetylates GABPB1, impairing GABPB1 heterotetramerization and activity (By similarity). In addition to protein acetyltransferase, can use different acyl-CoA substrates, such as (2E)-butenoyl-CoA (crotonyl-CoA), butanoyl-CoA (butyryl-CoA), 2-hydroxyisobutanoyl-CoA (2-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA) or propanoyl-CoA (propionyl-CoA), and is able to mediate protein crotonylation, butyrylation, 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation or propionylation, respectively. Acts as a histone crotonyltransferase; crotonylation marks active promoters and enhancers and confers resistance to transcriptional repressors. Histone crotonyltransferase activity is dependent on the concentration of (2E)-butenoyl-CoA (crotonyl-CoA) substrate and such activity is weak when (2E)-butenoyl-CoA (crotonyl-CoA) concentration is low. Also acts as a histone butyryltransferase; butyrylation marks active promoters. Acts as a protein-lysine 2-hydroxyisobutyryltransferase; regulates glycolysis by mediating 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation of glycolytic enzymes. Functions as a transcriptional coactivator for SMAD4 in the TGF-beta signaling pathway. Acetylates PCK1 and promotes PCK1 anaplerotic activity. Acetylates RXRA and RXRG.
(Microbial infection) In case of HIV-1 infection, it is recruited by the viral protein Tat. Regulates Tat's transactivating activity and may help inducing chromatin remodeling of proviral genes. Binds to and may be involved in the transforming capacity of the adenovirus E1A protein.
Acetylated on Lys at up to 17 positions by intermolecular autocatalysis. Deacetylated in the transcriptional repression domain (CRD1) by SIRT1, preferentially at Lys-1020. Deacetylated by SIRT2, preferentially at Lys-418, Lys-423, Lys-1542, Lys-1546, Lys-1549, Lys-1699, Lys-1704 and Lys-1707.
Citrullinated at Arg-2142 by PADI4, which impairs methylation by CARM1 and promotes interaction with NCOA2/GRIP1.
Methylated at Arg-580 and Arg-604 in the KIX domain by CARM1, which blocks association with CREB, inhibits CREB signaling and activates apoptotic response. Also methylated at Arg-2142 by CARM1, which impairs interaction with NCOA2/GRIP1.
Sumoylated; sumoylation in the transcriptional repression domain (CRD1) mediates transcriptional repression. Desumoylated by SENP3 through the removal of SUMO2 and SUMO3.
Probable target of ubiquitination by FBXO3, leading to rapid proteasome-dependent degradation.
Phosphorylated by HIPK2 in a RUNX1-dependent manner. This phosphorylation that activates EP300 happens when RUNX1 is associated with DNA and CBFB. Phosphorylated by ROCK2 and this enhances its activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-89 by AMPK reduces interaction with nuclear receptors, such as PPARG.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Chromosome.
Note: Localizes to active chromatin: Colocalizes with histone H3 acetylated and/or crotonylated at 'Lys-18' (H3K18ac and H3K18cr, respectively) (PubMed:25818647). In the presence of ALX1 relocalizes from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Colocalizes with ROCK2 in the nucleus (PubMed:12929931).
Interacts with phosphorylated CREB1. Interacts with HIF1A; the interaction is stimulated in response to hypoxia and inhibited by CITED2. Interacts (via N-terminus) with TFAP2A (via N-terminus); the interaction requires CITED2. Interacts (via CH1 domain) with CITED2 (via C-terminus). Interacts with CITED1 (unphosphorylated form preferentially and via C-terminus). Interacts with ESR1; the interaction is estrogen-dependent and enhanced by CITED1. Interacts with DTX1, EID1, ELF3, FEN1, LEF1, NCOA1, NCOA6, NR3C1, PCAF, PELP1, PRDM6, SP1, SP3, SPIB, SRY, TCF7L2, TP53, DDX5, DDX17, SATB1, SRCAP, TTC5, JMY and TRERF1. The TAZ-type 1 domain interacts with HIF1A. Probably part of a complex with HIF1A and CREBBP. Part of a complex containing CARM1 and NCOA2/GRIP1. Interacts with ING4 and this interaction may be indirect. Interacts with ING5. Interacts with the C-terminal region of CITED4. Non-sumoylated EP300 preferentially interacts with SENP3. Interacts with SS18L1/CREST. Interacts with ALX1 (via homeobox domain). Interacts with NEUROD1; the interaction is inhibited by NR0B2. Interacts with TCF3. Interacts (via CREB-binding domain) with MYOCD (via C-terminus). Binds to HIPK2. Interacts with ROCK2 and PPARG. Forms a complex made of CDK9, CCNT1/cyclin-T1, EP300 and GATA4 that stimulates hypertrophy in cardiomyocytes. Interacts with IRF1 and this interaction enhances acetylation of p53/TP53 and stimulation of its activity. Interacts with FOXO1; the interaction acetylates FOXO1 and enhances its transcriptional activity. Interacts with ALKBH4 and DDIT3/CHOP. Interacts with KLF15. Interacts with CEBPB and RORA. Interacts with p30II. Interacts with NPAS2, ARNTL/BMAL1 and CLOCK. Interacts with SIRT2 isoform 1, isoform 2 and isoform 5. Interacts with MTA1. Interacts with HDAC4 and HDAC5 in the presence of TFAP2C. Interacts with TRIP4. Directly interacts with ZBTB49; this interaction leads to synergistic transactivation of CDKN1A. Interacts with NR4A3 (By similarity). Interacts with ZNF451. Interacts with ATF5; EP300 is required for ATF5 and CEBPB interaction and DNA binding (By similarity). Interacts with HSF1. Interacts with ZBTB48/TZAP. Interacts with STAT1; the interaction is enhanced upon IFN-gamma stimulation. Interacts with HNRNPU (via C-terminus); this interaction enhances DNA-binding of HNRNPU to nuclear scaffold/matrix attachment region (S/MAR) elements. Interacts with BCL11B. Interacts with SMAD4; negatively regulated by ZBTB7A. Interacts with DUX4 (via C-terminus). Interacts with NUPR1; this interaction enhances the effect of EP300 on PAX2 transcription factor activity. Interacts with RXRA; the interaction is decreased by 9-cis retinoic acid. NR4A1 competes with EP300 for interaction with RXRA and thereby attenuates EP300 mediated acetylation of RXRA. Interacts with RB1 (By similarity). Interacts with DDX3X; this interaction may facilitate HNF4A acetylation.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with human adenovirus 5 E1A protein; this interaction stimulates the acetylation of RB1 by recruiting EP300 and RB1 into a multimeric-protein complex.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with and acetylates HIV-1 Tat.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HTLV-1 proteins Tax, p30II and HBZ.
The CRD1 domain (cell cycle regulatory domain 1) mediates transcriptional repression of a subset of p300 responsive genes; it can be de-repressed by CDKN1A/p21WAF1 at least at some promoters. It conatins sumoylation and acetylation sites and the same lysine residues may be targeted for the respective modifications. It is proposed that deacetylation by SIRT1 allows sumoylation leading to suppressed activity.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Notch signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Huntington's disease.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term potentiation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Glucagon signaling pathway.
文献引用
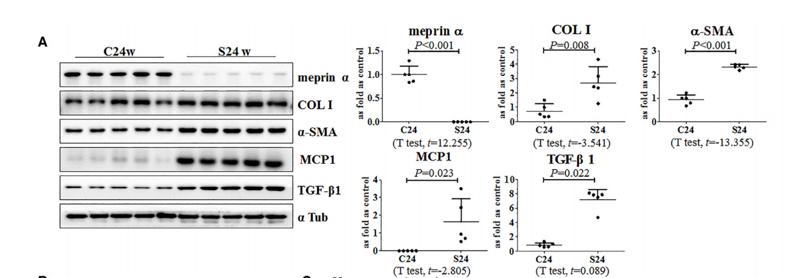
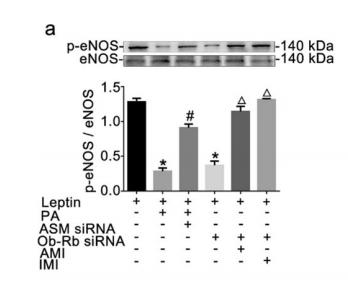
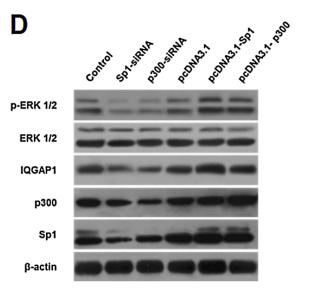
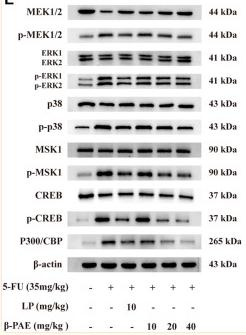
Application: WB Species: human Sample: PLC-PRF-5 cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: MSI2 and EP300 in SW620 and LOVO cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: myeloma cell
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Application: WB Species: human Sample: ADLI cell
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.