产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5368, RRID:AB_2837853.
展开/折叠
EL52; epididymis luminal secretory protein 52; Heat shock 86 kDa; heat shock 90kD protein 1, alpha; Heat shock 90kD protein 1, alpha like 4; heat shock 90kD protein, alpha-like 4; Heat shock 90kDa protein 1 alpha; Heat shock protein 90kDa alpha (cytosolic) class A member 1; Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha; HS90A_HUMAN; HSP 86; HSP86; Hsp89; HSP89A; Hsp90; HSP90A; HSP90AA1; HSP90ALPHA; HSP90N; HSPC1; HSPCA; HSPCAL1; HSPCAL4; HSPN; LAP 2; LAP2; lipopolysaccharide-associated protein 2; LPS-associated protein 2; Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-38;
抗原和靶标
- P07900 HS90A_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPEETQTQDQPMEEEEVETFAFQAEIAQLMSLIINTFYSNKEIFLRELISNSSDALDKIRYESLTDPSKLDSGKELHINLIPNKQDRTLTIVDTGIGMTKADLINNLGTIAKSGTKAFMEALQAGADISMIGQFGVGFYSAYLVAEKVTVITKHNDDEQYAWESSAGGSFTVRTDTGEPMGRGTKVILHLKEDQTEYLEERRIKEIVKKHSQFIGYPITLFVEKERDKEVSDDEAEEKEDKEEEKEKEEKESEDKPEIEDVGSDEEEEKKDGDKKKKKKIKEKYIDQEELNKTKPIWTRNPDDITNEEYGEFYKSLTNDWEDHLAVKHFSVEGQLEFRALLFVPRRAPFDLFENRKKKNNIKLYVRRVFIMDNCEELIPEYLNFIRGVVDSEDLPLNISREMLQQSKILKVIRKNLVKKCLELFTELAEDKENYKKFYEQFSKNIKLGIHEDSQNRKKLSELLRYYTSASGDEMVSLKDYCTRMKENQKHIYYITGETKDQVANSAFVERLRKHGLEVIYMIEPIDEYCVQQLKEFEGKTLVSVTKEGLELPEDEEEKKKQEEKKTKFENLCKIMKDILEKKVEKVVVSNRLVTSPCCIVTSTYGWTANMERIMKAQALRDNSTMGYMAAKKHLEINPDHSIIETLRQKAEADKNDKSVKDLVILLYETALLSSGFSLEDPQTHANRIYRMIKLGLGIDEDDPTADDTSAAVTEEMPPLEGDDDTSRMEEVD
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Molecular chaperone that promotes the maturation, structural maintenance and proper regulation of specific target proteins involved for instance in cell cycle control and signal transduction. Undergoes a functional cycle that is linked to its ATPase activity which is essential for its chaperone activity. This cycle probably induces conformational changes in the client proteins, thereby causing their activation. Interacts dynamically with various co-chaperones that modulate its substrate recognition, ATPase cycle and chaperone function. Engages with a range of client protein classes via its interaction with various co-chaperone proteins or complexes, that act as adapters, simultaneously able to interact with the specific client and the central chaperone itself. Recruitment of ATP and co-chaperone followed by client protein forms a functional chaperone. After the completion of the chaperoning process, properly folded client protein and co-chaperone leave HSP90 in an ADP-bound partially open conformation and finally, ADP is released from HSP90 which acquires an open conformation for the next cycle. Apart from its chaperone activity, it also plays a role in the regulation of the transcription machinery. HSP90 and its co-chaperones modulate transcription at least at three different levels. In the first place, they alter the steady-state levels of certain transcription factors in response to various physiological cues. Second, they modulate the activity of certain epigenetic modifiers, such as histone deacetylases or DNA methyl transferases, and thereby respond to the change in the environment. Third, they participate in the eviction of histones from the promoter region of certain genes and thereby turn on gene expression. Binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and mediates LPS-induced inflammatory response, including TNF secretion by monocytes. Antagonizes STUB1-mediated inhibition of TGF-beta signaling via inhibition of STUB1-mediated SMAD3 ubiquitination and degradation.
ISGylated.
S-nitrosylated; negatively regulates the ATPase activity and the activation of eNOS by HSP90AA1.
Ubiquitinated via 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination by HECTD1. Ubiquitination promotes translocation into the cytoplasm away from the membrane and secretory pathways.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Melanosome. Cell membrane.
Note: Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV.
Homodimer. Identified in NR3C1/GCR steroid receptor-chaperone complexes formed at least by NR3C1, HSP90AA1 and a variety of proteins containing TPR repeats such as FKBP4, FKBP5, PPID, PPP5C or STIP1. Forms a complex containing HSP90AA1, TSC1 and TSC2; TSC1 is required to recruit TCS2 to the complex. The closed form interacts (via the middle domain and TPR repeat-binding motif) with co-chaperone TSC1 (via C-terminus). Interacts with TOM34. Interacts with TERT; the interaction, together with PTGES3, is required for correct assembly and stabilization of the TERT holoenzyme complex. Interacts with CHORDC1 and DNAJC7. Interacts with STUB1 and UBE2N; may couple the chaperone and ubiquitination systems. Interacts (via TPR repeat-binding motif) with PPP5C (via TPR repeats); the interaction is direct and activates PPP5C phosphatase activity. Following LPS binding, may form a complex with CXCR4, GDF5 and HSPA8. Interacts with KSR1. Interacts with co-chaperone CDC37 (via C-terminus); the interaction inhibits HSP90AA1 ATPase activity. May interact with NWD1. Interacts with FNIP1 and FNIP2; the interaction inhibits HSP90AA1 ATPase activity. Interacts with co-chaperone AHSA1 (phosphorylated on 'Tyr-223'); the interaction activates HSP90AA1 ATPase activity and results in the dissociation of TSC1 from HSP90AA1. Interacts with FLCN in the presence of FNIP1. Interacts with HSP70, STIP1 and PTGES3. Interacts with SMYD3; this interaction enhances SMYD3 histone-lysine N-methyltransferase. Interacts with SGTA (via TPR repeats). Interacts with TTC1 (via TPR repeats). Interacts with HSF1 in an ATP-dependent manner.. Interacts with MET; the interaction suppresses MET kinase activity. Interacts with ERBB2 in an ATP-dependent manner; the interaction suppresses ERBB2 kinase activity. Interacts with HIF1A, KEAP1 and RHOBTB2. Interacts with HSF1; this interaction is decreased in a IER5-dependent manner, promoting HSF1 accumulation in the nucleus, homotrimerization and DNA-binding activities. Interacts with STUB1 and SMAD3. Interacts with HSP90AB1; interaction is constitutive. Interacts with HECTD1 (via N-terminus) (By similarity). Interacts with NR3C1 (via domain NR LBD) and NR1D1 (via domain NR LBD) (By similarity). Interacts with NLPR12. Interacts with PDCL3 (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Interacts with herpes simplex virus 1 protein US11; this interaction inhibits TBK1-induced interferon production.
The TPR repeat-binding motif mediates interaction with TPR repeat-containing proteins like the co-chaperone STUB1.
Belongs to the heat shock protein 90 family.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Antigen processing and presentation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
文献引用
Application: IHC Species: human Sample: HCC cells
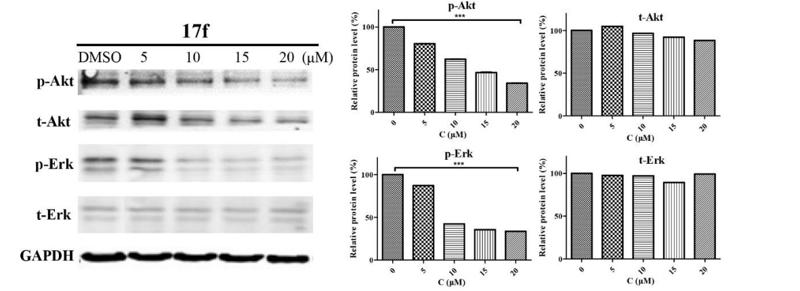
Application: WB Species: human Sample: PLC-PRF-5 cells
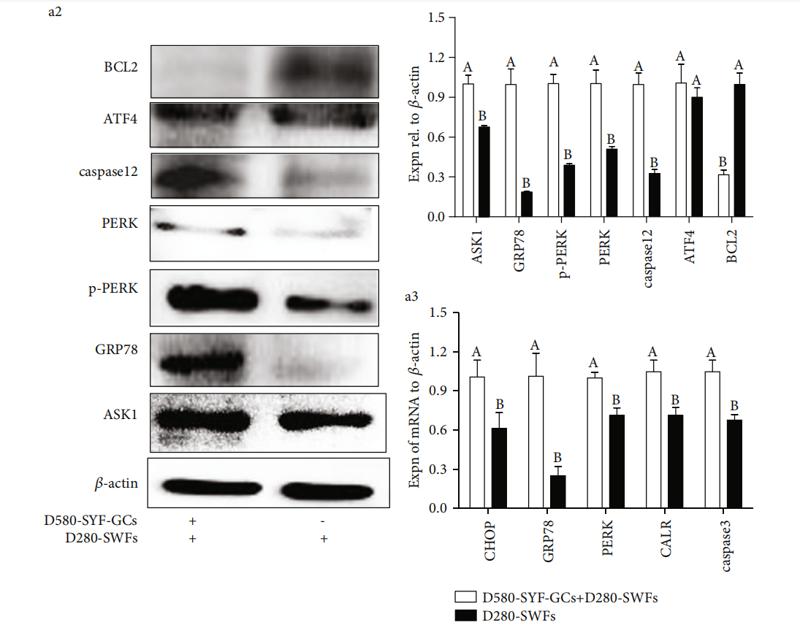
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: CAFs and 4T1cells
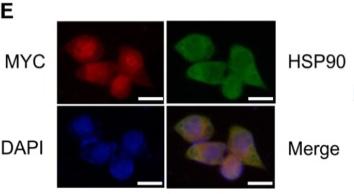
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: Eca-109 cells
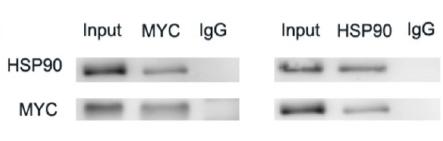
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: Eca-109 cells
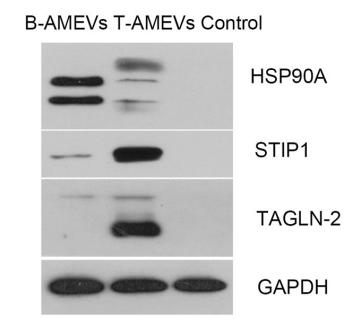
Application: WB Species: human Sample: T‑AMEVs and B‑AMEVs
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.