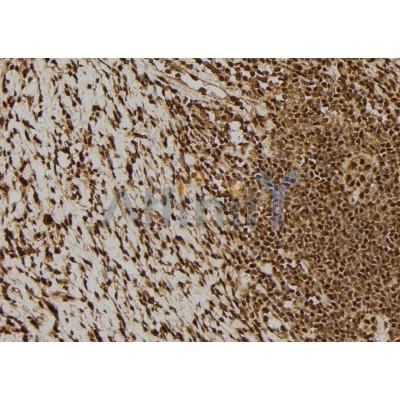
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6015, RRID:AB_2837990.
展开/折叠
Apoptosis regulator Bcl X; Apoptosis regulator Bcl-X; Apoptosis regulator BclX; B cell lymphoma 2 like; B2CL1_HUMAN; Bcl 2 like 1 protein; Bcl X; Bcl xL; BCL XL/S; Bcl xS; Bcl-2-like protein 1; Bcl2 Like 1; Bcl2 related gene; Bcl2-L-1; BCL2L; Bcl2l1; BCLX; BclXL; BclXs; DKFZp781P2092; PPP1R52; Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 52;
抗原和靶标
Bcl-X(S) is expressed at high levels in cells that undergo a high rate of turnover, such as developing lymphocytes. In contrast, Bcl-X(L) is found in tissues containing long-lived postmitotic cells, such as adult brain.
- Q07817 B2CL1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSQSNRELVVDFLSYKLSQKGYSWSQFSDVEENRTEAPEGTESEMETPSAINGNPSWHLADSPAVNGATGHSSSLDAREVIPMAAVKQALREAGDEFELRYRRAFSDLTSQLHITPGTAYQSFEQVVNELFRDGVNWGRIVAFFSFGGALCVESVDKEMQVLVSRIAAWMATYLNDHLEPWIQENGGWDTFVELYGNNAAAESRKGQERFNRWFLTGMTVAGVVLLGSLFSRK
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Potent inhibitor of cell death. Inhibits activation of caspases. Appears to regulate cell death by blocking the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) by binding to it and preventing the release of the caspase activator, CYC1, from the mitochondrial membrane. Also acts as a regulator of G2 checkpoint and progression to cytokinesis during mitosis.
Isoform Bcl-X(L) also regulates presynaptic plasticity, including neurotransmitter release and recovery, number of axonal mitochondria as well as size and number of synaptic vesicle clusters. During synaptic stimulation, increases ATP availability from mitochondria through regulation of mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase F(1)F(0) activity and regulates endocytic vesicle retrieval in hippocampal neurons through association with DMN1L and stimulation of its GTPase activity in synaptic vesicles. May attenuate inflammation impairing NLRP1-inflammasome activation, hence CASP1 activation and IL1B release.
Isoform Bcl-X(S) promotes apoptosis.
Proteolytically cleaved by caspases during apoptosis. The cleaved protein, lacking the BH4 motif, has pro-apoptotic activity.
Phosphorylated on Ser-62 by CDK1. This phosphorylation is partial in normal mitotic cells, but complete in G2-arrested cells upon DNA-damage, thus promoting subsequent apoptosis probably by triggering caspases-mediated proteolysis. Phosphorylated by PLK3, leading to regulate the G2 checkpoint and progression to cytokinesis during mitosis. Phosphorylation at Ser-49 appears during the S phase and G2, disappears rapidly in early mitosis during prometaphase, metaphase and early anaphase, and re-appears during telophase and cytokinesis.
Ubiquitinated by RNF183 during prolonged ER stress, leading to degradation by the proteosome.
Mitochondrion inner membrane. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Mitochondrion matrix. Cytoplasmic vesicle>Secretory vesicle>Synaptic vesicle membrane. Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Nucleus membrane>Single-pass membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side.
Note: After neuronal stimulation, translocates from cytosol to synaptic vesicle and mitochondrion membrane in a calmodulin-dependent manner (By similarity). Localizes to the centrosome when phosphorylated at Ser-49.
Bcl-X(S) is expressed at high levels in cells that undergo a high rate of turnover, such as developing lymphocytes. In contrast, Bcl-X(L) is found in tissues containing long-lived postmitotic cells, such as adult brain.
Homodimer. Isoform Bcl-X(L) forms heterodimers with BAX, BAK or BCL2. Heterodimerization with BAX does not seem to be required for anti-apoptotic activity. Interacts with BCL2L11. Interacts with BAD. Interacts (isoform Bcl-X(L)) with SIVA1 (isoform 1); the interaction inhibits the anti-apoptotic activity. Interacts with BECN1 and PGAM5. Isoform Bcl-X(L) interacts with IKZF3. Interacts with HEBP2. Isoform Bcl-X(L) interacts with RTL10/BOP. Interacts with p53/TP53 and BBC3; interaction with BBC3 disrupts the interaction with p53/TP53. Isoform Bcl-X(L) interacts with DNM1L and CLTA; DNM1L and BCL2L1 isoform BCL-X(L) may form a complex in synaptic vesicles that also contains clathrin and MFF. Interacts with ATP5F1A and ATP5F1B; the interactions mediate the association of isoform Bcl-X(L) with the mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase F(1)F(0) ATP synthase. Interacts with VDAC1. Isoform Bcl-X(L) interacts (via the loop between motifs BH4 and BH3) with NLRP1 (via LRR repeats), but not with NLRP2, NLRP3, NLRP4, PYCARD, nor MEFV. Interacts with BCL2L11 (via BH3). Interacts with RNF183. Interacts with GIMAP3/IAN4 and GIMAP5/IAN5. Interacts with GIMAP5 and HSPA8/HSC70; the interaction between HSPA8 and BCL2L1 is impaired in the absence of GIMAP5 (By similarity). Interacts with CLU (isoform 4); this interaction releases and activates BAX and promotes cell death.
The BH4 motif is required for anti-apoptotic activity. The BH1 and BH2 motifs are required for both heterodimerization with other Bcl-2 family members and for repression of cell death.
The loop between motifs BH4 and BH3 is required for the interaction with NLRP1.
Belongs to the Bcl-2 family.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Platinum drug resistance.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
文献引用
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HK-2 Cells
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.