pan Actin Antibody - #AF0115
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0115, RRID:AB_2833265.
展开/折叠
A26C1A; A26C1B; ACTB; ACTB_HUMAN; Actin beta; Actin cytoplasmic 1; Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed; Actx; b actin; Beta cytoskeletal actin; Beta-actin; BRWS1; E430023M04Rik; MGC128179; PS1TP5 binding protein 1; PS1TP5BP1; ACT; ACTBL3; FKSG30; POTE ankyrin domain family member K pseudogene; POTE2delta; POTEK; ACT; ACTB; ACTG; ACTG_HUMAN; actg1; Actin; Actin, cytoplasmic 2; Actin, gamma 1; Actin, gamma 1 propeptide; Actin, gamma; BRWS2; cytoplasmic 2; Cytoskeletal gamma actin; Deafness, autosomal dominant 20; Deafness, autosomal dominant 26; DFNA20; DFNA26; epididymis luminal protein 176; Gamma-actin; HEL-176; N-terminally processed;
抗原和靶标
A synthesized peptide derived from human Actin-pan.
- P60709 ACTB_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDDDIAALVVDNGSGMCKAGFAGDDAPRAVFPSIVGRPRHQGVMVGMGQKDSYVGDEAQSKRGILTLKYPIEHGIVTNWDDMEKIWHHTFYNELRVAPEEHPVLLTEAPLNPKANREKMTQIMFETFNTPAMYVAIQAVLSLYASGRTTGIVMDSGDGVTHTVPIYEGYALPHAILRLDLAGRDLTDYLMKILTERGYSFTTTAEREIVRDIKEKLCYVALDFEQEMATAASSSSLEKSYELPDGQVITIGNERFRCPEALFQPSFLGMESCGIHETTFNSIMKCDVDIRKDLYANTVLSGGTTMYPGIADRMQKEITALAPSTMKIKIIAPPERKYSVWIGGSILASLSTFQQMWISKQEYDESGPSIVHRKCF
- Q9BYX7 ACTBM_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDDDTAVLVIDNGSGMCKAGFAGDDAPQAVFPSIVGRPRHQGMMEGMHQKESYVGKEAQSKRGMLTLKYPMEHGIITNWDDMEKIWHHTFYNELRVAPEEHPILLTEAPLNPKANREKMTQIMFETFNTPAMYVAIQAVLSLYTSGRTTGIVMDSGDGFTHTVPIYEGNALPHATLRLDLAGRELTDYLMKILTERGYRFTTTAEQEIVRDIKEKLCYVALDSEQEMAMAASSSSVEKSYELPDGQVITIGNERFRCPEALFQPCFLGMESCGIHKTTFNSIVKSDVDIRKDLYTNTVLSGGTTMYPGIAHRMQKEITALAPSIMKIKIIAPPKRKYSVWVGGSILASLSTFQQMWISKQEYDESGPSIVHRKCF
- P63261 ACTG_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEEEIAALVIDNGSGMCKAGFAGDDAPRAVFPSIVGRPRHQGVMVGMGQKDSYVGDEAQSKRGILTLKYPIEHGIVTNWDDMEKIWHHTFYNELRVAPEEHPVLLTEAPLNPKANREKMTQIMFETFNTPAMYVAIQAVLSLYASGRTTGIVMDSGDGVTHTVPIYEGYALPHAILRLDLAGRDLTDYLMKILTERGYSFTTTAEREIVRDIKEKLCYVALDFEQEMATAASSSSLEKSYELPDGQVITIGNERFRCPEALFQPSFLGMESCGIHETTFNSIMKCDVDIRKDLYANTVLSGGTTMYPGIADRMQKEITALAPSTMKIKIIAPPERKYSVWIGGSILASLSTFQQMWISKQEYDESGPSIVHRKCF
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Actin is a highly conserved protein that polymerizes to produce filaments that form cross-linked networks in the cytoplasm of cells. Actin exists in both monomeric (G-actin) and polymeric (F-actin) forms, both forms playing key functions, such as cell motility and contraction. In addition to their role in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton, G- and F-actin also localize in the nucleus, and regulate gene transcription and motility and repair of damaged DNA.
ISGylated.
Oxidation of Met-44 and Met-47 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. MICAL1 and MICAL2 produce the (R)-S-oxide form. The (R)-S-oxide form is reverted by MSRB1 and MSRB2, which promote actin repolymerization.
Monomethylation at Lys-84 (K84me1) regulates actin-myosin interaction and actomyosin-dependent processes. Demethylation by ALKBH4 is required for maintaining actomyosin dynamics supporting normal cleavage furrow ingression during cytokinesis and cell migration.
Methylated at His-73 by SETD3. Methylation at His-73 is required for smooth muscle contraction of the laboring uterus during delivery (By similarity).
N-terminal acetylation by NAA80 affects actin filament depolymerization and elongation, including elongation driven by formins. In contrast, filament nucleation by the Arp2/3 complex is not affected.
(Microbial infection) Monomeric actin is cross-linked by V.cholerae toxins RtxA and VgrG1 in case of infection: bacterial toxins mediate the cross-link between Lys-50 of one monomer and Glu-270 of another actin monomer, resulting in formation of highly toxic actin oligomers that cause cell rounding. The toxin can be highly efficient at very low concentrations by acting on formin homology family proteins: toxic actin oligomers bind with high affinity to formins and adversely affect both nucleation and elongation abilities of formins, causing their potent inhibition in both profilin-dependent and independent manners.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Nucleus.
Note: Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs.
Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to 4 others. Identified in a IGF2BP1-dependent mRNP granule complex containing untranslated mRNAs. Component of the BAF complex, which includes at least actin (ACTB), ARID1A, ARID1B/BAF250, SMARCA2, SMARCA4/BRG1, ACTL6A/BAF53, ACTL6B/BAF53B, SMARCE1/BAF57 SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCC2/BAF170, SMARCB1/SNF5/INI1, and one or more of SMARCD1/BAF60A, SMARCD2/BAF60B, or SMARCD3/BAF60C. In muscle cells, the BAF complex also contains DPF3. Found in a complex with XPO6, Ran, ACTB and PFN1. Interacts with XPO6 and EMD. Interacts with ERBB2. Interacts with GCSAM. Interacts with TBC1D21 (By similarity). Interacts with CPNE1 (via VWFA domain) and CPNE4 (via VWFA domain) (By similarity). Interacts with DHX9 (via C-terminus); this interaction is direct and mediates the attachment to nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes. Interacts with FAM107A.
Belongs to the actin family.
Oxidation of Met-44 and Met-47 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. MICAL1 and MICAL2 produce the (R)-S-oxide form. The (R)-S-oxide form is reverted by MSRB1 and MSRB2, which promote actin repolymerization (By similarity).
Monomethylation at Lys-84 (K84me1) regulates actin-myosin interaction and actomyosin-dependent processes. Demethylation by ALKBH4 is required for maintaining actomyosin dynamics supporting normal cleavage furrow ingression during cytokinesis and cell migration.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Expressed in some hepatocellular carcinomas.
Interacts with PFN1 and PFDN1. Does not interact with PFN2.
Belongs to the actin family.
Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
Oxidation of Met-44 and Met-47 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. MICAL1 and MICAL2 produce the (R)-S-oxide form. The (R)-S-oxide form is reverted by MSRB1 and MSRB2, which promote actin repolymerization.
Monomethylation at Lys-84 (K84me1) regulates actin-myosin interaction and actomyosin-dependent processes. Demethylation by ALKBH4 is required for maintaining actomyosin dynamics supporting normal cleavage furrow ingression during cytokinesis and cell migration.
N-terminal acetylation by NAA80 affects actin filament depolymerization and elongation, including elongation driven by formins. In contrast, filament nucleation by the Arp2/3 complex is not affected.
Methylated at His-73 by SETD3.
(Microbial infection) Monomeric actin is cross-linked by V.cholerae toxins RtxA and VgrG1 in case of infection: bacterial toxins mediate the cross-link between Lys-50 of one monomer and Glu-270 of another actin monomer, resulting in formation of highly toxic actin oligomers that cause cell rounding. The toxin can be highly efficient at very low concentrations by acting on formin homology family proteins: toxic actin oligomers bind with high affinity to formins and adversely affect both nucleation and elongation abilities of formins, causing their potent inhibition in both profilin-dependent and independent manners.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to 4 others. Interacts with TWF1, CAPZB, cofilin and profilin.
Belongs to the actin family.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Vibrio cholerae infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Shigellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Viral myocarditis.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Leukocyte transendothelial migration. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Gastric acid secretion.
文献引用
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: testes
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: γδ T Cells
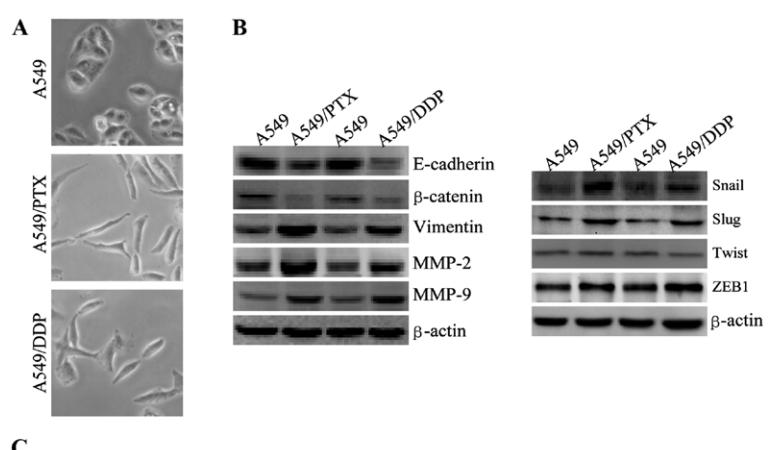
Application: WB Species: human Sample: A549 cells
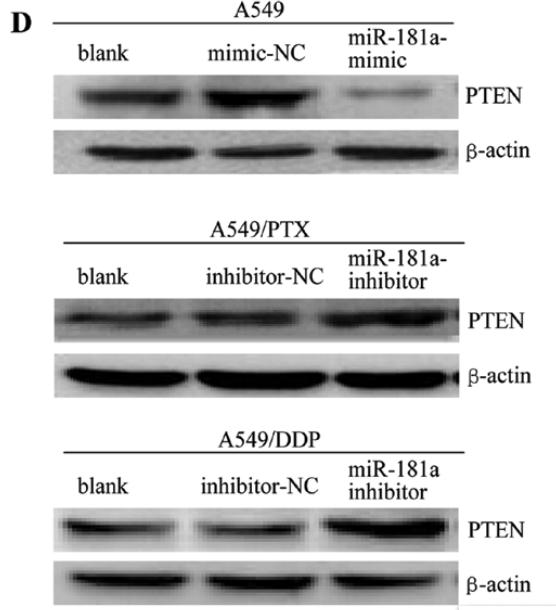
Application: WB Species: human Sample: A549, A549/PTX or A549/DDP cells
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.