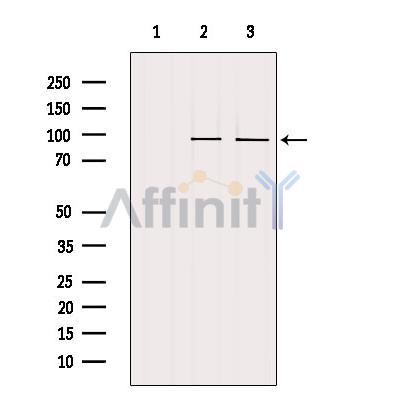
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6929, RRID:AB_2838888.
展开/折叠
Ac2-121; AL022808; E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UHRF1; EC 6.3.2.-; FLJ21925; hNP95; hUHRF1; HuNp95; ICBP90; Inverted CCAAT box binding protein of 90 kDa; Inverted CCAAT box binding protein, 90-kD; Inverted CCAAT box-binding protein of 90 kDa; Liver regeneration-related protein LRRG126; MGC138707; NP95; Nuclear phosphoprotein 95; Nuclear phosphoprotein, 95-KD; Nuclear protein 95; Nuclear zinc finger protein Np95; RING finger protein 106; RNF106; TDRD22; Transcription factor ICBP90; Ubiquitin like containing PHD and RING finger domains protein 1; Ubiquitin like PHD and RING finger domain containing protein 1; Ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing protein 1; Ubiquitin-like protein containing PHD and RING finger domains 1; Ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1; Ubiquitin-like, containing PHD and RING finger domains, 1; Ubiquitin-like-containing PHD and RING finger domains protein 1; UHRF1; UHRF1_HUMAN;
抗原和靶标
Expressed in thymus, bone marrow, testis, lung and heart. Overexpressed in breast cancer.
- Q96T88 UHRF1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MWIQVRTMDGRQTHTVDSLSRLTKVEELRRKIQELFHVEPGLQRLFYRGKQMEDGHTLFDYEVRLNDTIQLLVRQSLVLPHSTKERDSELSDTDSGCCLGQSESDKSSTHGEAAAETDSRPADEDMWDETELGLYKVNEYVDARDTNMGAWFEAQVVRVTRKAPSRDEPCSSTSRPALEEDVIYHVKYDDYPENGVVQMNSRDVRARARTIIKWQDLEVGQVVMLNYNPDNPKERGFWYDAEISRKRETRTARELYANVVLGDDSLNDCRIIFVDEVFKIERPGEGSPMVDNPMRRKSGPSCKHCKDDVNRLCRVCACHLCGGRQDPDKQLMCDECDMAFHIYCLDPPLSSVPSEDEWYCPECRNDASEVVLAGERLRESKKKAKMASATSSSQRDWGKGMACVGRTKECTIVPSNHYGPIPGIPVGTMWRFRVQVSESGVHRPHVAGIHGRSNDGAYSLVLAGGYEDDVDHGNFFTYTGSGGRDLSGNKRTAEQSCDQKLTNTNRALALNCFAPINDQEGAEAKDWRSGKPVRVVRNVKGGKNSKYAPAEGNRYDGIYKVVKYWPEKGKSGFLVWRYLLRRDDDEPGPWTKEGKDRIKKLGLTMQYPEGYLEALANREREKENSKREEEEQQEGGFASPRTGKGKWKRKSAGGGPSRAGSPRRTSKKTKVEPYSLTAQQSSLIREDKSNAKLWNEVLASLKDRPASGSPFQLFLSKVEETFQCICCQELVFRPITTVCQHNVCKDCLDRSFRAQVFSCPACRYDLGRSYAMQVNQPLQTVLNQLFPGYGNGR
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
翻译修饰 - Q96T88 作为底物
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| T13 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K24 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K24 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K31 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K50 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T68 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S76 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K84 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S88 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S91 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T93 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S95 | Phosphorylation | P48730 (CSNK1D) | Uniprot |
| S104 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S108 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T117 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S119 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K136 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S165 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K233 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S265 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S287 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S298 | Phosphorylation | P17612 (PRKACA) | Uniprot |
| K303 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K306 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S368 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K385 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K385 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S393 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K399 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K399 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K399 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K408 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y418 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T492 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S496 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C497 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K500 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K500 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K525 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K525 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K531 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K546 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K546 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K546 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K560 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K563 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K563 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K568 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K570 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K570 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K592 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K600 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K600 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K626 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K626 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S639 | Phosphorylation | P06493 (CDK1) | Uniprot |
| K650 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| S651 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R658 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| S661 | Phosphorylation | P24941 (CDK2) | Uniprot |
| K670 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K670 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S682 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K692 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K692 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K702 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S707 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S709 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S751 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot |
研究背景
Multidomain protein that acts as a key epigenetic regulator by bridging DNA methylation and chromatin modification. Specifically recognizes and binds hemimethylated DNA at replication forks via its YDG domain and recruits DNMT1 methyltransferase to ensure faithful propagation of the DNA methylation patterns through DNA replication. In addition to its role in maintenance of DNA methylation, also plays a key role in chromatin modification: through its tudor-like regions and PHD-type zinc fingers, specifically recognizes and binds histone H3 trimethylated at 'Lys-9' (H3K9me3) and unmethylated at 'Arg-2' (H3R2me0), respectively, and recruits chromatin proteins. Enriched in pericentric heterochromatin where it recruits different chromatin modifiers required for this chromatin replication. Also localizes to euchromatic regions where it negatively regulates transcription possibly by impacting DNA methylation and histone modifications. Has E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity by mediating the ubiquitination of target proteins such as histone H3 and PML. It is still unclear how E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity is related to its role in chromatin in vivo. May be involved in DNA repair.
Phosphorylation at Ser-298 of the linker region decreases the binding to H3K9me3. Phosphorylation at Ser-639 by CDK1 during M phase impairs interaction with USP7, preventing deubiquitination and leading to degradation by the proteasome.
Ubiquitinated; which leads to proteasomal degradation. Autoubiquitinated; interaction with USP7 leads to deubiquitination and prevents degradation. Ubiquitination and degradation takes place during M phase, when phosphorylation at Ser-639 prevents interaction with USP7 and subsequent deubiquitination. Polyubiquitination may be stimulated by DNA damage.
Nucleus.
Note: Localizes to replication foci. Enriched in pericentric heterochromatin. Also localizes to euchromatic regions.
Expressed in thymus, bone marrow, testis, lung and heart. Overexpressed in breast cancer.
Interacts with DNMT3A and DNMT3B (By similarity). Interacts with DNMT1; the interaction is direct. Interacts with USP7; leading to its deubiquitination. Interacts with histone H3. Interacts with HDAC1, but not with HDAC2. Interacts with UHRF1BP1. Interacts with PML. Interacts with EHMT2. Binds hemimethylated CpG containing oligonucleotides.
The tudor-like regions specifically recognize and bind histone H3 unmethylated at 'Arg-2' (H3R2me0), while the PHD-type zinc finger specifically recognizes and binds histone H3 trimethylated at 'Lys-9' (H3K9me3). The tudor-like regions simultaneously recognizes H3K9me3 through a conserved aromatic cage in the first tudor-like subdomain and unmodified H3K4 (H3K4me0) within a groove between the tandem subdomains (PubMed:21489993, PubMed:21777816 and PubMed:22100450). The linker region plays a role in the formation of a histone H3-binding hole between the reader modules formed by the tudor-like regions and the PHD-type zinc finger by making extended contacts with the tandem tudor-like regions (PubMed:22837395).
The YDG domain (also named SRA domain) specifically recognizes and binds hemimethylated DNA at replication forks (DNA that is only methylated on the mother strand of replicating DNA) (PubMed:17673620). It contains a binding pocket that accommodates the 5-methylcytosine that is flipped out of the duplex DNA. 2 specialized loops reach through the resulting gap in the DNA from both the major and the minor grooves to read the other 3 bases of the CpG duplex. The major groove loop confers both specificity for the CpG dinucleotide and discrimination against methylation of deoxycytidine of the complementary strand (PubMed:18772889). The YDG domain also recognizes and binds 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) (PubMed:21731699).
The RING finger is required for ubiquitin ligase activity.
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.