产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7100, RRID:AB_2839055.
展开/折叠
Damage-specific DNA-binding protein 1; DDB p127 subunit; Ddb1; DDB1_HUMAN; DDBa; DNA damage-binding protein 1; DNA damage-binding protein a; HBV X-associated protein 1; UV-damaged DNA-binding factor; UV-damaged DNA-binding protein 1; UV-DDB 1; XAP-1; Xeroderma pigmentosum group E-complementing protein; XPCe; XPE-BF; XPE-binding factor;
抗原和靶标
- Q16531 DDB1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSYNYVVTAQKPTAVNGCVTGHFTSAEDLNLLIAKNTRLEIYVVTAEGLRPVKEVGMYGKIAVMELFRPKGESKDLLFILTAKYNACILEYKQSGESIDIITRAHGNVQDRIGRPSETGIIGIIDPECRMIGLRLYDGLFKVIPLDRDNKELKAFNIRLEELHVIDVKFLYGCQAPTICFVYQDPQGRHVKTYEVSLREKEFNKGPWKQENVEAEASMVIAVPEPFGGAIIIGQESITYHNGDKYLAIAPPIIKQSTIVCHNRVDPNGSRYLLGDMEGRLFMLLLEKEEQMDGTVTLKDLRVELLGETSIAECLTYLDNGVVFVGSRLGDSQLVKLNVDSNEQGSYVVAMETFTNLGPIVDMCVVDLERQGQGQLVTCSGAFKEGSLRIIRNGIGIHEHASIDLPGIKGLWPLRSDPNRETDDTLVLSFVGQTRVLMLNGEEVEETELMGFVDDQQTFFCGNVAHQQLIQITSASVRLVSQEPKALVSEWKEPQAKNISVASCNSSQVVVAVGRALYYLQIHPQELRQISHTEMEHEVACLDITPLGDSNGLSPLCAIGLWTDISARILKLPSFELLHKEMLGGEIIPRSILMTTFESSHYLLCALGDGALFYFGLNIETGLLSDRKKVTLGTQPTVLRTFRSLSTTNVFACSDRPTVIYSSNHKLVFSNVNLKEVNYMCPLNSDGYPDSLALANNSTLTIGTIDEIQKLHIRTVPLYESPRKICYQEVSQCFGVLSSRIEVQDTSGGTTALRPSASTQALSSSVSSSKLFSSSTAPHETSFGEEVEVHNLLIIDQHTFEVLHAHQFLQNEYALSLVSCKLGKDPNTYFIVGTAMVYPEEAEPKQGRIVVFQYSDGKLQTVAEKEVKGAVYSMVEFNGKLLASINSTVRLYEWTTEKELRTECNHYNNIMALYLKTKGDFILVGDLMRSVLLLAYKPMEGNFEEIARDFNPNWMSAVEILDDDNFLGAENAFNLFVCQKDSAATTDEERQHLQEVGLFHLGEFVNVFCHGSLVMQNLGETSTPTQGSVLFGTVNGMIGLVTSLSESWYNLLLDMQNRLNKVIKSVGKIEHSFWRSFHTERKTEPATGFIDGDLIESFLDISRPKMQEVVANLQYDDGSGMKREATADDLIKVVEELTRIH
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Required for DNA repair. Binds to DDB2 to form the UV-damaged DNA-binding protein complex (the UV-DDB complex). The UV-DDB complex may recognize UV-induced DNA damage and recruit proteins of the nucleotide excision repair pathway (the NER pathway) to initiate DNA repair. The UV-DDB complex preferentially binds to cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD), 6-4 photoproducts (6-4 PP), apurinic sites and short mismatches. Also appears to function as a component of numerous distinct DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes which mediate the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. The functional specificity of the DCX E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex is determined by the variable substrate recognition component recruited by DDB1. DCX(DDB2) (also known as DDB1-CUL4-ROC1, CUL4-DDB-ROC1 and CUL4-DDB-RBX1) may ubiquitinate histone H2A, histone H3 and histone H4 at sites of UV-induced DNA damage. The ubiquitination of histones may facilitate their removal from the nucleosome and promote subsequent DNA repair. DCX(DDB2) also ubiquitinates XPC, which may enhance DNA-binding by XPC and promote NER. DCX(DTL) plays a role in PCNA-dependent polyubiquitination of CDT1 and MDM2-dependent ubiquitination of TP53 in response to radiation-induced DNA damage and during DNA replication. DCX(ERCC8) (the CSA complex) plays a role in transcription-coupled repair (TCR). The DDB1-CUL4A-DTL E3 ligase complex regulates the circadian clock function by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of CRY1. DDB1-mediated CRY1 degradation promotes FOXO1 protein stability and FOXO1-mediated gluconeogenesis in the liver (By similarity).
Phosphorylated by ABL1.
Ubiquitinated by CUL4A. Subsequently degraded by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis.
Acetylated, promoting interaction with CUL4 (CUL4A or CUL4B) and subsequent formation of DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes. Deacetylation by SIRT7 impairs the interaction with CUL4 (CUL4A or CUL4B) and formation of DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Primarily cytoplasmic. Translocates to the nucleus following UV irradiation and subsequently accumulates at sites of DNA damage.
Component of the UV-DDB complex which includes DDB1 and DDB2; the heterodimer dimerizes to give rise to a heterotetramer when bound to damaged DNA. The UV-DDB complex interacts with monoubiquitinated histone H2A and binds to XPC via the DDB2 subunit. Component of numerous DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes which consist of a core of DDB1, CUL4A or CUL4B and RBX1. DDB1 may recruit specific substrate targeting subunits to the DCX complex. These substrate targeting subunits are generally known as DCAF (DDB1- and CUL4-associated factor) or CDW (CUL4-DDB1-associated WD40-repeat) proteins. Interacts with AMBRA1, ATG16L1, BTRC, CRBN, DCAF1, DCAF4, DCAF5, DCAF6, DCAF7, DCAF8, DCAF9, DCAF10, DCAF11, DCAF12, DCAF15, DCAF16, DCAF17, DDA1, DET1, DTL, ERCC8, FBXW5, FBXW8, GRWD1, KATNB1, NLE1, NUP43, PAFAH1B1, PHIP, PWP1, RBBP4, RBBP5, RBBP7, COP1, SNRNP40, DCAF1, WDR5, WDR5B, WDR12, WDR26, WDR39, WDR42, WDR53, WDR59, WDR61, WSB1, WSB2, LRWD1 and WDTC1. DCX complexes may associate with the COP9 signalosome, and this inhibits the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of the complex. Interacts with NF2, TSC1 and TSC2. Interaction with SV5 protein V may prevent the recruitment of DCAF proteins to DCX complexes. Interacts with AGO1 and AGO2. Associates with the E3 ligase complex containing DYRK2, EDD/UBR5, DDB1 and DCAF1 proteins (EDVP complex). Interacts directly with DYRK2. DCX(DTL) complex interacts with FBXO11; does not ubiquitinate and degradate FBXO11. Interacts with TRPC4AP. Interacts with CRY1 and CRY2 (By similarity). The DDB1-CUL4A complex interacts with CRY1.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Simian virus 5 protein V.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with hepatitis B virus protein HBX; the viral protein contains a short helical motif that competes for the same binding site as the N-terminal helical motif found in endogenous DCAF proteins.
The core of the protein consists of three WD40 beta-propeller domains.
Belongs to the DDB1 family.
研究领域
· Genetic Information Processing > Replication and repair > Nucleotide excision repair.
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
文献引用
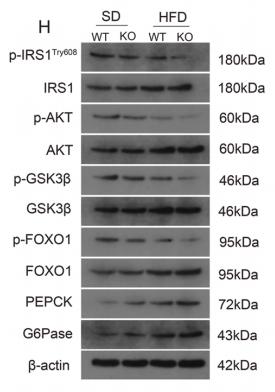
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: liver
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.