产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0047, RRID:AB_2834093.
展开/折叠
c Raf; C-raf; C-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase; CMD1NN; Craf 1 transforming gene; cRaf; Craf1 transforming gene; EC 2.7.11.1; kinase Raf1; Murine sarcoma 3611 oncogene 1; NS5; Oncogene MIL; Oncogene RAF1; OTTHUMP00000160218; OTTHUMP00000207813; OTTHUMP00000209389; Protein kinase raf 1; Proto-oncogene c-RAF; Raf 1; Raf 1 proto oncogene serine/threonine kinase; RAF; Raf proto oncogene serine/threonine protein kinase; RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase; RAF-1; RAF1; RAF1_HUMAN; Similar to murine leukemia viral (V-raf-1) oncogene homolog 1; TRANSFORMING REPLICATION-DEFECTIVE MURINE RETROVIRUS 3611-MSV; v raf 1 murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1; v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1; v-raf-1 murine leukemia viral oncogene-like protein 1; vraf1 murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1;
抗原和靶标
A synthesized peptide derived from human C-RAF around the phosphorylation site of Ser301.
- P04049 RAF1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEHIQGAWKTISNGFGFKDAVFDGSSCISPTIVQQFGYQRRASDDGKLTDPSKTSNTIRVFLPNKQRTVVNVRNGMSLHDCLMKALKVRGLQPECCAVFRLLHEHKGKKARLDWNTDAASLIGEELQVDFLDHVPLTTHNFARKTFLKLAFCDICQKFLLNGFRCQTCGYKFHEHCSTKVPTMCVDWSNIRQLLLFPNSTIGDSGVPALPSLTMRRMRESVSRMPVSSQHRYSTPHAFTFNTSSPSSEGSLSQRQRSTSTPNVHMVSTTLPVDSRMIEDAIRSHSESASPSALSSSPNNLSPTGWSQPKTPVPAQRERAPVSGTQEKNKIRPRGQRDSSYYWEIEASEVMLSTRIGSGSFGTVYKGKWHGDVAVKILKVVDPTPEQFQAFRNEVAVLRKTRHVNILLFMGYMTKDNLAIVTQWCEGSSLYKHLHVQETKFQMFQLIDIARQTAQGMDYLHAKNIIHRDMKSNNIFLHEGLTVKIGDFGLATVKSRWSGSQQVEQPTGSVLWMAPEVIRMQDNNPFSFQSDVYSYGIVLYELMTGELPYSHINNRDQIIFMVGRGYASPDLSKLYKNCPKAMKRLVADCVKKVKEERPLFPQILSSIELLQHSLPKINRSASEPSLHRAAHTEDINACTLTTSPRLPVF
研究背景
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts as a regulatory link between the membrane-associated Ras GTPases and the MAPK/ERK cascade, and this critical regulatory link functions as a switch determining cell fate decisions including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, survival and oncogenic transformation. RAF1 activation initiates a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade that comprises a sequential phosphorylation of the dual-specific MAPK kinases (MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2) and the extracellular signal-regulated kinases (MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2). The phosphorylated form of RAF1 (on residues Ser-338 and Ser-339, by PAK1) phosphorylates BAD/Bcl2-antagonist of cell death at 'Ser-75'. Phosphorylates adenylyl cyclases: ADCY2, ADCY5 and ADCY6, resulting in their activation. Phosphorylates PPP1R12A resulting in inhibition of the phosphatase activity. Phosphorylates TNNT2/cardiac muscle troponin T. Can promote NF-kB activation and inhibit signal transducers involved in motility (ROCK2), apoptosis (MAP3K5/ASK1 and STK3/MST2), proliferation and angiogenesis (RB1). Can protect cells from apoptosis also by translocating to the mitochondria where it binds BCL2 and displaces BAD/Bcl2-antagonist of cell death. Regulates Rho signaling and migration, and is required for normal wound healing. Plays a role in the oncogenic transformation of epithelial cells via repression of the TJ protein, occludin (OCLN) by inducing the up-regulation of a transcriptional repressor SNAI2/SLUG, which induces down-regulation of OCLN. Restricts caspase activation in response to selected stimuli, notably Fas stimulation, pathogen-mediated macrophage apoptosis, and erythroid differentiation.
Phosphorylation at Thr-269, Ser-338, Tyr-341, Thr-491 and Ser-494 results in its activation. Phosphorylation at Ser-29, Ser-43, Ser-289, Ser-296, Ser-301 and Ser-642 by MAPK1/ERK2 results in its inactivation. Phosphorylation at Ser-259 induces the interaction with YWHAZ and inactivates kinase activity. Dephosphorylation of Ser-259 by the complex containing protein phosphatase 1, SHOC2 and M-Ras/MRAS relieves inactivation, leading to stimulate RAF1 activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-338 by PAK1 and PAK5 and Ser-339 by PAK1 is required for its mitochondrial localization. Phosphorylation at Ser-621 in response to growth factor treatment stabilizes the protein, possibly by preventing proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylation at Ser-289, Ser-296, Ser-301, Ser-338 and Ser-621 are somehow linked to the methylation potential of cells. Treatment of cells with HGF in the presence of the methylation inhibitor 5'-methylthioadenosine (MTA) results in increased phosphorylation at Ser-338 and Ser-621 and decreased phosphorylation at Ser-296, Ser-301 and Ser-338. Dephosphorylation at Ser-338 by PPP5C results in an activity decrease.
Methylated at Arg-563 in response to EGF treatment. This modification leads to destabilization of the protein, possibly through proteasomal degradation.
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Mitochondrion. Nucleus.
Note: Colocalizes with RGS14 and BRAF in both the cytoplasm and membranes. Phosphorylation at Ser-259 impairs its membrane accumulation. Recruited to the cell membrane by the active Ras protein. Phosphorylation at Ser-338 and Ser-339 by PAK1 is required for its mitochondrial localization. Retinoic acid-induced Ser-621 phosphorylated form of RAF1 is predominantly localized at the nucleus.
In skeletal muscle, isoform 1 is more abundant than isoform 2.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family. RAF subfamily.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Sphingolipid signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Phospholipase D signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > mTOR signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Alcoholism.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Endometrial cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Bladder cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Central carbon metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Vascular smooth muscle contraction. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term potentiation.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Serotonergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term depression.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Prolactin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
文献引用
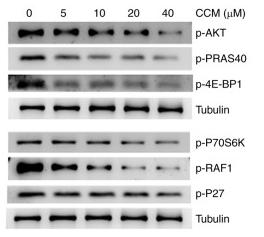
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: ML-2 cells
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.