Tubulin alpha Antibody - #AF0524
产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0524, RRID:AB_2834165.
展开/折叠
Alpha tubulin 3; Alpha-tubulin 3; B alpha 1; FLJ25113; LIS3; TBA1A_HUMAN; TUBA1A; TUBA3; Tubulin alpha 1a; Tubulin alpha 1A chain; Tubulin alpha 3; Tubulin alpha 3 chain; Tubulin alpha brain specific; Tubulin alpha-1A chain; Tubulin alpha-3 chain; Tubulin B alpha 1; Tubulin B-alpha-1; Alpha tubulin ubiquitous; Alpha-tubulin ubiquitous; K alpha 1; TBA1B_HUMAN; TUBA1B; Tubulin alpha 1B; Tubulin alpha 1B chain; Tubulin alpha ubiquitous; Tubulin alpha ubiquitous chain; Tubulin alpha-1B chain; Tubulin alpha-ubiquitous chain; Tubulin K alpha 1; Tubulin K-alpha-1;
抗原和靶标
- Q71U36 TBA1A_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRECISIHVGQAGVQIGNACWELYCLEHGIQPDGQMPSDKTIGGGDDSFNTFFSETGAGKHVPRAVFVDLEPTVIDEVRTGTYRQLFHPEQLITGKEDAANNYARGHYTIGKEIIDLVLDRIRKLADQCTGLQGFLVFHSFGGGTGSGFTSLLMERLSVDYGKKSKLEFSIYPAPQVSTAVVEPYNSILTTHTTLEHSDCAFMVDNEAIYDICRRNLDIERPTYTNLNRLIGQIVSSITASLRFDGALNVDLTEFQTNLVPYPRIHFPLATYAPVISAEKAYHEQLSVAEITNACFEPANQMVKCDPRHGKYMACCLLYRGDVVPKDVNAAIATIKTKRTIQFVDWCPTGFKVGINYQPPTVVPGGDLAKVQRAVCMLSNTTAIAEAWARLDHKFDLMYAKRAFVHWYVGEGMEEGEFSEAREDMAALEKDYEEVGVDSVEGEGEEEGEEY
- P68363 TBA1B_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRECISIHVGQAGVQIGNACWELYCLEHGIQPDGQMPSDKTIGGGDDSFNTFFSETGAGKHVPRAVFVDLEPTVIDEVRTGTYRQLFHPEQLITGKEDAANNYARGHYTIGKEIIDLVLDRIRKLADQCTGLQGFLVFHSFGGGTGSGFTSLLMERLSVDYGKKSKLEFSIYPAPQVSTAVVEPYNSILTTHTTLEHSDCAFMVDNEAIYDICRRNLDIERPTYTNLNRLISQIVSSITASLRFDGALNVDLTEFQTNLVPYPRIHFPLATYAPVISAEKAYHEQLSVAEITNACFEPANQMVKCDPRHGKYMACCLLYRGDVVPKDVNAAIATIKTKRSIQFVDWCPTGFKVGINYQPPTVVPGGDLAKVQRAVCMLSNTTAIAEAWARLDHKFDLMYAKRAFVHWYVGEGMEEGEFSEAREDMAALEKDYEEVGVDSVEGEGEEEGEEY
种属预测
score>80的预测可信度较高,可尝试用于WB检测。*预测模型主要基于免疫原序列比对,结果仅作参考,不作为质保凭据。
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
研究背景
Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are polyglutamylated, resulting in polyglutamate chains on the gamma-carboxyl group. Polyglutamylation plays a key role in microtubule severing by spastin (SPAST). SPAST preferentially recognizes and acts on microtubules decorated with short polyglutamate tails: severing activity by SPAST increases as the number of glutamates per tubulin rises from one to eight, but decreases beyond this glutamylation threshold.
Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are monoglycylated but not polyglycylated due to the absence of functional TTLL10 in human. Monoglycylation is mainly limited to tubulin incorporated into axonemes (cilia and flagella). Both polyglutamylation and monoglycylation can coexist on the same protein on adjacent residues, and lowering glycylation levels increases polyglutamylation, and reciprocally. The precise function of monoglycylation is still unclear (Probable).
Acetylation of alpha chains at Lys-40 is located inside the microtubule lumen. This modification has been correlated with increased microtubule stability, intracellular transport and ciliary assembly.
Methylation of alpha chains at Lys-40 is found in mitotic microtubules and is required for normal mitosis and cytokinesis contributing to genomic stability.
Nitration of Tyr-451 is irreversible and interferes with normal dynein intracellular distribution.
Undergoes a tyrosination/detyrosination cycle, the cyclic removal and re-addition of a C-terminal tyrosine residue by the enzymes tubulin tyrosine carboxypeptidase (VASH1 or VASH2) and tubulin tyrosine ligase (TTL), respectively.
Tyrosination promotes microtubule interaction with CAP-Gly domain-containing proteins such as CLIP1, CLIP2 and DCTN1. Tyrosination regulates the initiation of dynein-dynactin motility via interaction with DCTN1, which brings the dynein-dynactin complex into contact with microtubules. In neurons, tyrosinated tubulins mediate the initiation of retrograde vesicle transport.
Detyrosination is involved in metaphase plate congression by guiding chromosomes during mitosis: detyrosination promotes interaction with CENPE, promoting pole-proximal transport of chromosomes toward the equator. Detyrosination increases microtubules-dependent mechanotransduction in dystrophic cardiac and skeletal muscle. In cardiomyocytes, detyrosinated microtubules are required to resist to contractile compression during contraction: detyrosination promotes association with desmin (DES) at force-generating sarcomeres, leading to buckled microtubules and mechanical resistance to contraction (By similarity).
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Expressed at a high level in fetal brain.
Dimer of alpha and beta chains. A typical microtubule is a hollow water-filled tube with an outer diameter of 25 nm and an inner diameter of 15 nM. Alpha-beta heterodimers associate head-to-tail to form protofilaments running lengthwise along the microtubule wall with the beta-tubulin subunit facing the microtubule plus end conferring a structural polarity. Microtubules usually have 13 protofilaments but different protofilament numbers can be found in some organisms and specialized cells. Interacts with SETD2; the interaction is independent on alpha-tubulin acetylation on Lys-40.
Belongs to the tubulin family.
Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are polyglutamylated, resulting in polyglutamate chains on the gamma-carboxyl group. Polyglutamylation plays a key role in microtubule severing by spastin (SPAST). SPAST preferentially recognizes and acts on microtubules decorated with short polyglutamate tails: severing activity by SPAST increases as the number of glutamates per tubulin rises from one to eight, but decreases beyond this glutamylation threshold.
Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are monoglycylated but not polyglycylated due to the absence of functional TTLL10 in human. Monoglycylation is mainly limited to tubulin incorporated into axonemes (cilia and flagella). Both polyglutamylation and monoglycylation can coexist on the same protein on adjacent residues, and lowering glycylation levels increases polyglutamylation, and reciprocally. The precise function of monoglycylation is still unclear (Probable).
Acetylation of alpha chains at Lys-40 is located inside the microtubule lumen. This modification has been correlated with increased microtubule stability, intracellular transport and ciliary assembly.
Methylation of alpha chains at Lys-40 is found in mitotic microtubules and is required for normal mitosis and cytokinesis contributing to genomic stability.
Nitration of Tyr-451 is irreversible and interferes with normal dynein intracellular distribution.
Undergoes a tyrosination/detyrosination cycle, the cyclic removal and re-addition of a C-terminal tyrosine residue by the enzymes tubulin tyrosine carboxypeptidase (VASH1 or VASH2) and tubulin tyrosine ligase (TTL), respectively.
Tyrosination promotes microtubule interaction with CAP-Gly domain-containing proteins such as CLIP1, CLIP2 and DCTN1 (By similarity). Tyrosination regulates the initiation of dynein-dynactin motility via interaction with DCTN1, which brings the dynein-dynactin complex into contact with microtubules. In neurons, tyrosinated tubulins mediate the initiation of retrograde vesicle transport (By similarity).
Detyrosination is involved in metaphase plate congression by guiding chromosomes during mitosis: detyrosination promotes interaction with CENPE, promoting pole-proximal transport of chromosomes toward the equator. Detyrosination increases microtubules-dependent mechanotransduction in dystrophic cardiac and skeletal muscle. In cardiomyocytes, detyrosinated microtubules are required to resist to contractile compression during contraction: detyrosination promotes association with desmin (DES) at force-generating sarcomeres, leading to buckled microtubules and mechanical resistance to contraction (By similarity).
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Dimer of alpha and beta chains. A typical microtubule is a hollow water-filled tube with an outer diameter of 25 nm and an inner diameter of 15 nM. Alpha-beta heterodimers associate head-to-tail to form protofilaments running lengthwise along the microtubule wall with the beta-tubulin subunit facing the microtubule plus end conferring a structural polarity. Microtubules usually have 13 protofilaments but different protofilament numbers can be found in some organisms and specialized cells.
Belongs to the tubulin family.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
文献引用
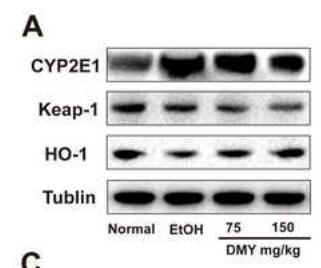
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.